CNC Drilling – Everything You Need to Know
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is CNC Drilling?
CNC drilling is a computer controlled process used for drilling holes in different materials. Manual drilling involves relying on human inputs to drill, but automated movement eliminates the human error and promotes accuracy. This method increases efficiency and is therefore critical in modern manufacturing. CNC drills make precise components in industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics and construction. The process delivers consistent results whether you’re drilling engine parts, circuit boards, or structural elements.

How Does CNC Drilling Work?
A drill machine cnc converts a digital design into a perfectly drilled part through a series of automated steps. Each stage guarantees hole placement with accuracy and quality. The detailed plan, material selection, programming, setup drilling and final inspection are part of the process. Below are key stages:

Key Stages of CNC Drilling
Design & Planning
First, design and planning. It begins with you building a 3D model in CAD software that lets you specify the exact dimensions, number and location of holes, and other specifications of the part. This digital blueprint is the base for the whole drilling process. Once the design is finalised you determine the hole placements, depths and sizes which are required to meet the functional needs of the component.
Material Selection
Material selection follows next. The material you choose is important because it controls the durability, performance and the machinability of the final product. Choosing the proper material for the CNC drill machine and intended purpose will lead to a successful project, whether you are working with metal, plastics, or composites.
Programming the CNC Machine
After the design and material are finalized you start programming the CNC machine. Once the CAD design is completed, the G-code is converted, which describes the movement, speed and drilling depth. This code is generated by CAM software that controls all drill cnc actions for precise hole placement.
Machine Setup
Once programming is completed, you set up the CNC machine. It involves picking the best drill bit, securing the workpiece with fixtures, and calibrating the machine for proper accuracy. Errors are minimized and the drilling process is smooth through proper setup.
Drilling Execution
The core of the drilling machining process is execution. The holes are drilled with high precision using the programmed G code. Different drilling cycles can be used according to requirement. G73 is a chip breaking cycle which prevents chip accumulation in deep holes. For standard hole depth, G81, shallow hole cycle ensures clean drilling. A pecking cycle such as G83 is useful for very deep holes to remove chips efficiently and maintain accuracy. During this phase continuous monitoring is taken to make sure that the drilling is on track.
Quality Inspection & Post-Processing
The post processing and quality inspection finish the process. After drilling, you may deburr the edges to remove sharp burrs or surface finish to meet the desired texture. Hole dimensions, alignment and smoothness are all quality control checks to verify that the final product meets the required specifications. The role of each stage is critical in the delivery of a precise, high-quality, drilled component.
What Are the Different CNC Drilling Operations?
Precision hole-making is a vital step in CNC machining and a first step to making precise holes into different materials. Different drilling operations are used for accuracy, surface finish, and thread formation. In this section you’ll look into the major automated drilling operations.
Types of CNC Drilling Operations
| Sr. No. | Operation | Description | Technical Specifications | Applications |
| 1 | Spot Drilling | Creates a small indentation to guide the drill bit. | Shallow depth, precise location. | Initial setup for drilling, ensuring accuracy. |
| 2 | Drilling | Creates cylindrical holes using a rotating drill bit. | Variable hole sizes and depths, depending on drill bit. | General hole creation in various materials. |
| 3 | Reaming | Enlarges and refines pre-drilled holes for accuracy and smoothness. | Tight tolerances, high surface finish. | Precise hole diameters, aerospace, automotive. |
| 4 | Boring | Enlarges existing holes to precise diameters. | High accuracy, customizable hole sizes. | Precision hole enlargement, specialized manufacturing. |
| 5 | Counterboring | Creates a stepped hole for flush fastener seating. | Specific diameters and depths for fastener heads. | Assembly processes requiring flush fasteners. |
| 6 | Countersinking | Creates a conical hole for flush screw heads. | Specific angles and depths for screw heads. | Assembly processes requiring smooth surfaces. |
| 7 | Tapping | Creates internal threads for bolts or screws. | Precise thread dimensions, pitch, and depth. | Threaded hole creation for secure fastening. |
| 8 | Micro-Drilling | Creates extremely small holes. | Micrometer-level precision, specialized machines. | Electronics, medical devices, intricate components. |
| 9 | Center Drilling | Creates a conical hole for drill bit guidance. | Conical shape, specific hole location. | Preparatory step for deep drilling, alignment. |
| 10 | Peck Drilling | Deep hole drilling with periodic drill bit retraction. | Chip evacuation, coolant flow, reduced heat buildup. | Deep hole drilling, materials prone to chip packing. |
| 11 | Gun Drilling | Deep, straight hole drilling with high precision. | Long, thin drill bits, internal coolant channels. | Hydraulic systems, aerospace, medical equipment. |
| 12 | Vibratory Drilling | Drilling with drill bit oscillation for improved cutting. | Controlled vibration frequencies, enhanced tool life. | Difficult-to-machine materials, optimized material removal. |
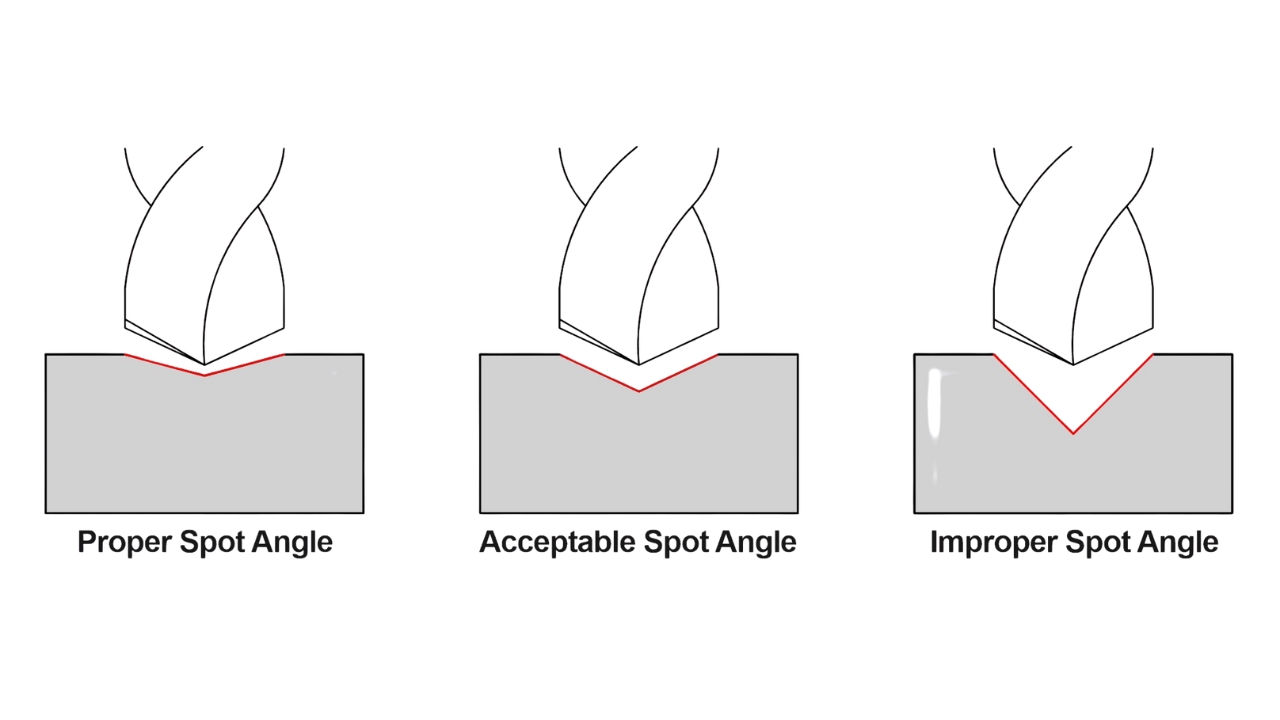
1. Spot Drilling
A guide hole for subsequent drilling is created by spot drilling. A shallow mark is made using a short drill bit that prevents the main drill from wandering. This step improves precision especially in high tolerance machining. In modern machining centres for drilling, spot drilling ensures the main drill enters accurately and maintains consistency across large production runs.
2. Drilling
The most common way of creating cylindrical holes on a workpiece is drilling, using a rotating drill bit. This can be used to form holes in metal, plastics and composites of various sizes and depths. This method ensures a high level of mass production, both in time and in quality.

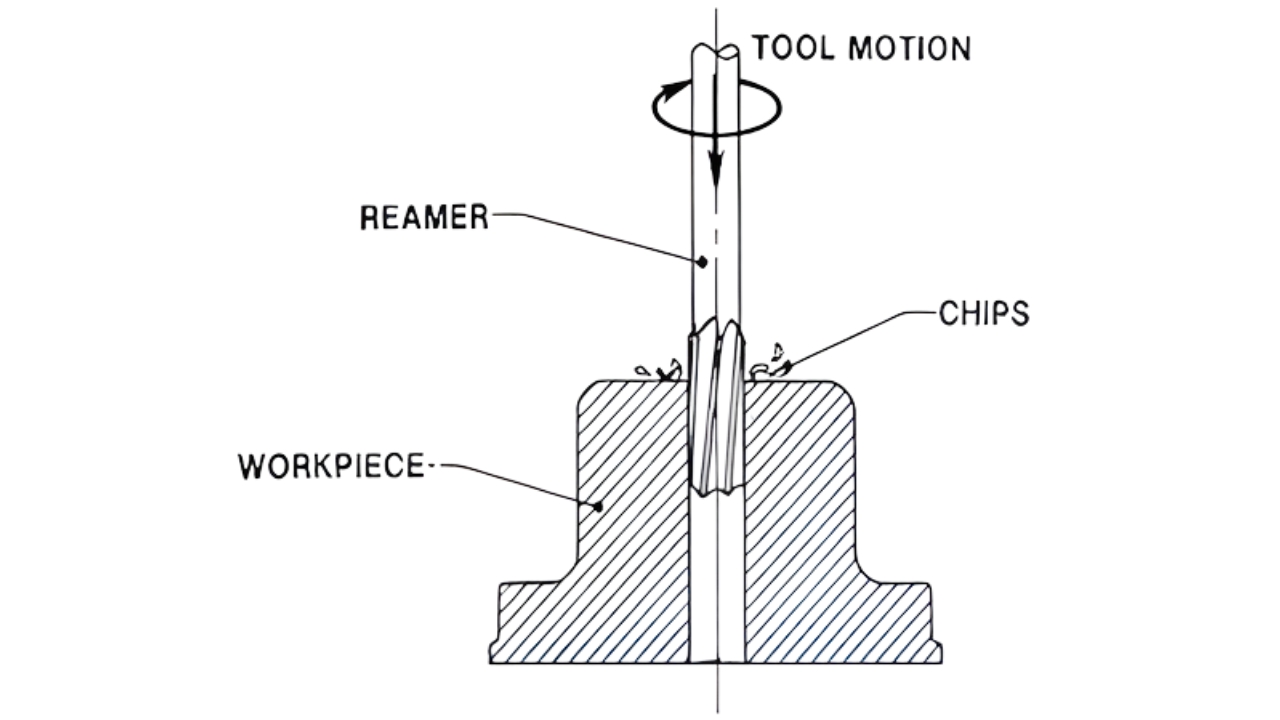
3. Reaming
The pre-drilled hole diameter accuracy and smoothness improves with reaming. The hole is refined using a reamer to tight tolerances. It is essential in aerospace as well as automotive industries where precision is paramount.
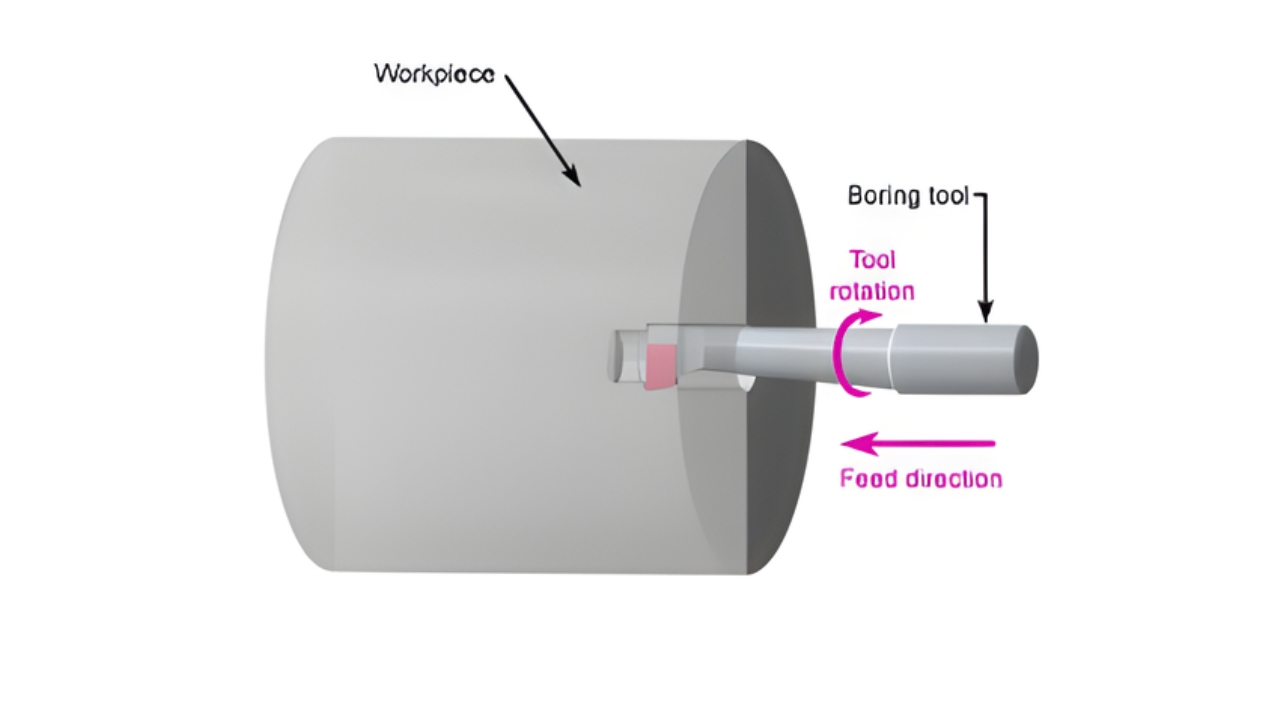
4. Boring
Boring is an operation in which an existing hole is enlarged to a precise diameter with high accuracy. The hole size is refined by you using a single point cutting tool. For very tight tolerances this method is ideal.
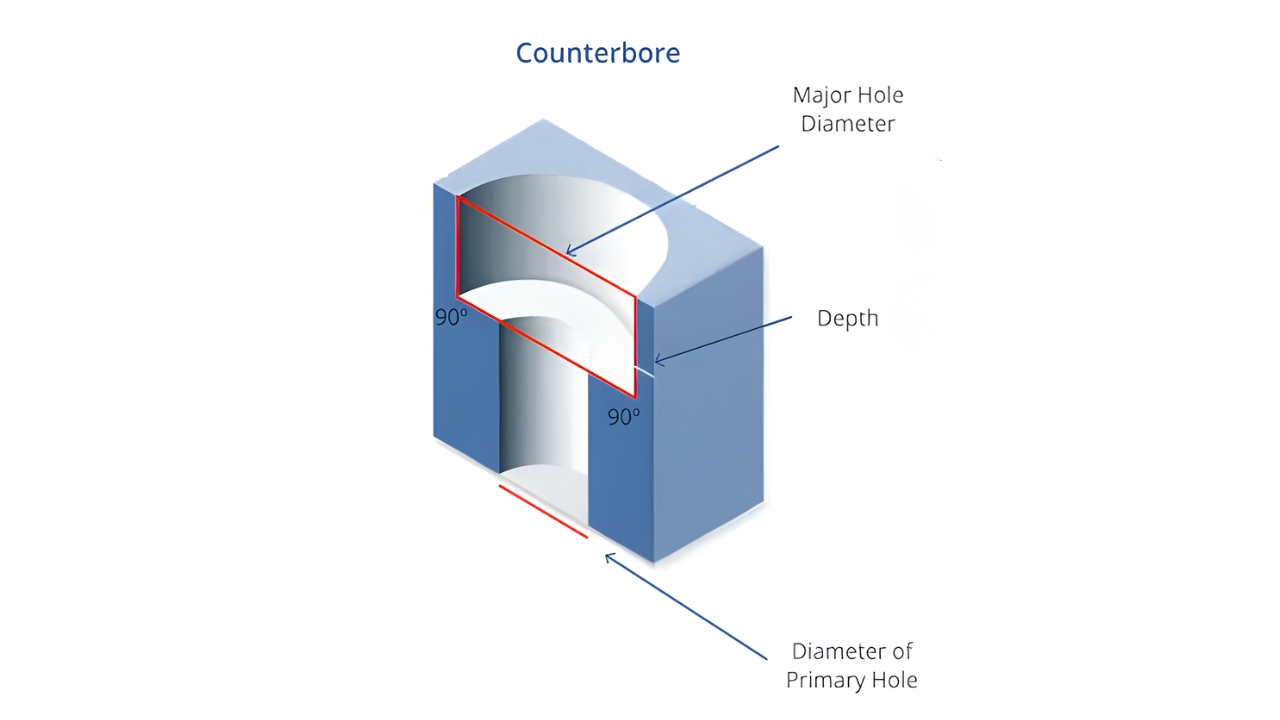
5. Counterboring
Counterboring creates a stepped hole that the screw head sits flush on the surface. The top part of a hole is enlarged using a counterbore tool. It is necessary for securing fasteners without protrusion.
6. Countersinking
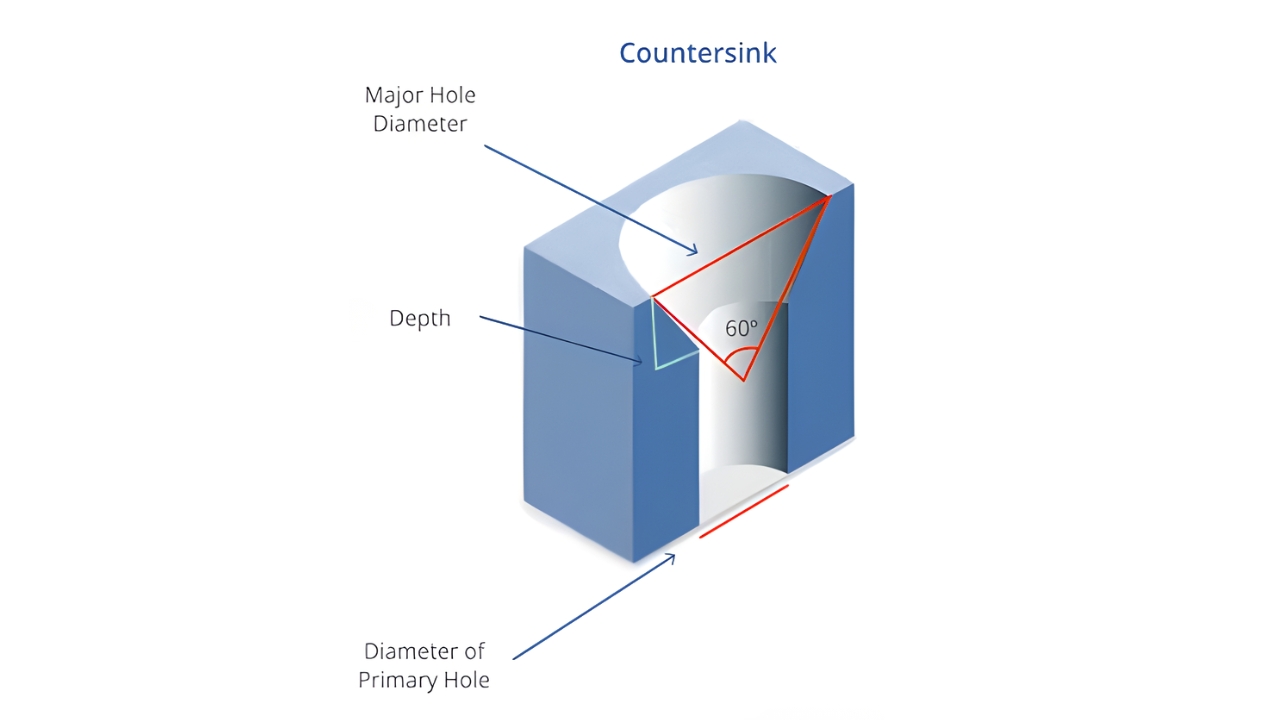
Flathead screws require screwed countersinking, which produces a conical hole. A countersink tool is used to make an angled surface to ensure that screws sit flush. It also improves functionality and aesthetics in assemblies.
7. Tapping
It involves tapping inside a pre drilled hole and it forms internal threads that allow bolts and screws to fit securely. To cut threads exactly, you use a tap tool. In manufacturing and assembly operations, this method is used widely.

8. Micro-Drilling
Very small holes are created by micro drilling, which is often in the micrometer range. For precision, you use fine drill bits and specialized CNC machines. That is crucial in electronics, medical devices, and aerospace applications.
9. Center Drilling
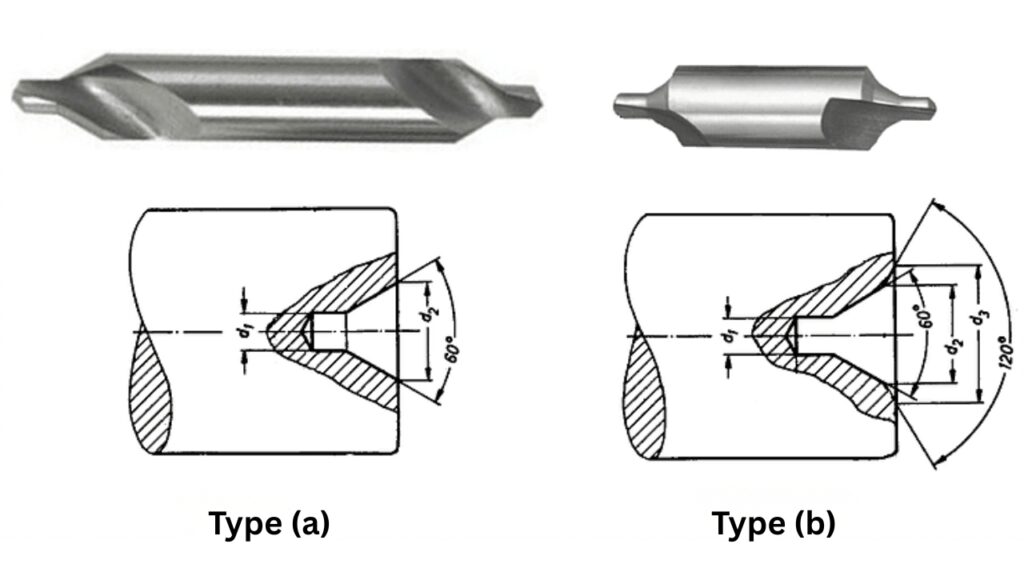
Deep drilling is guided by a small conical hole made by center drilling. Using a center drill, you align and prevent deviation. This technique is also essential for precision machining and deep hole drilling.
10. Peck Drilling
The deep-hole drilling with peck drilling improves chip removal. So, you periodically retract the drill bit, breaking and removing chips which reduces heat buildup. It results in improved tool life and hole quality, particularly in tough materials.
11. Gun Drilling
Deep and straight holes with very high precision can be drilled using gun drilling. Accuracy requires the use of a long, thin drill bit with internal coolant channels. This method is widely used in hydraulic systems and in firearm manufacturing.
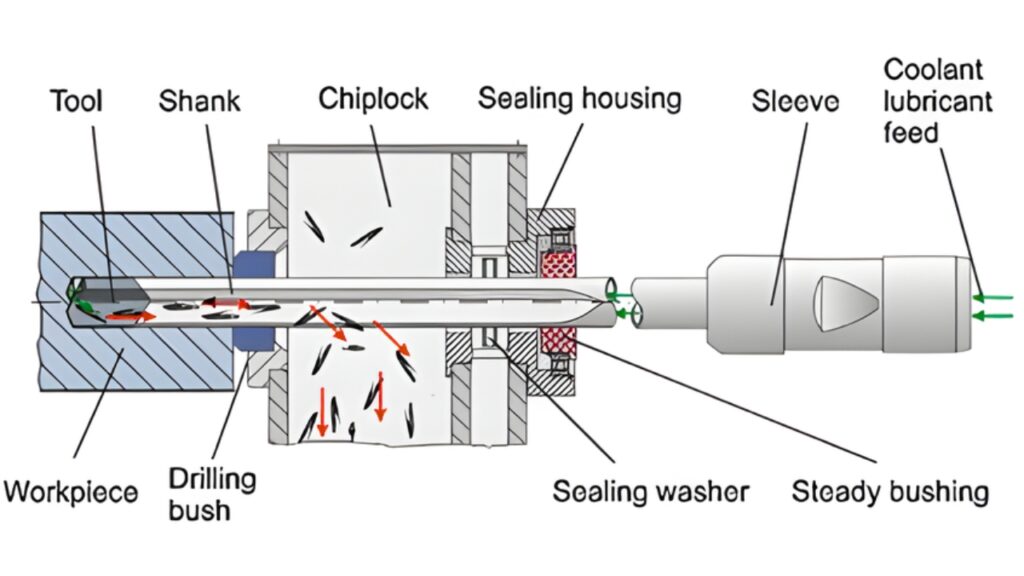
12. Vibratory Drilling
Controlled vibrations improve the efficiency of vibratory drilling. Oscillations are used to optimize material removal and reduce tool wear. Machining hard materials with higher productivity is ideal of this process.
What Are the Key Components of a CNC Drilling Machine?
An accurate, efficient, and smooth operation of CNC drills depends on several important components. Knowing these parts helps you improve drilling performance and to maintain the machine properly.
Control Panel: Here, you will input commands and control the drilling. It translates your design into the precise machine movements used in every operation.
Spindle: It rotates the drill bit and is used to determine drilling precision. The speed and power of the machine directly determine how well the machine cuts through different materials.
Drill Bits: These cutting tools drill holes in the workpiece. When drilling, you pick drill bits depending on material type and hole size for efficient and accurate drilling.
Worktable: The workpiece is supported by the worktable, which moves the workpiece beneath the drill bit. With this controlled movement, you are able to drill complex patterns with high precision.
Motor: The spindle motor runs and is affected by drilling speed and torque. Efficiency is increased with a powerful motor so it’s a breeze to drill through tough materials.
Tool Changer: During operations, this automatic system swaps drill bits. This will allow you to carry out several drilling operations without interruptions, reaching higher efficiency and reducing manual effort.
Supporting Systems
Coolant System: Heat from drilling machining can damage tools and materials. The coolant system ensures adequate temperature, to avoid overheating and to increase tool life.
Chip Removal System: It is important to remove chips from the drilling area for the operation to be smooth. This system clears debris and prevents blockages, and this is what gives this system its precision.
Sensors & Feedback Mechanisms: These components perform monitoring, error detection, and control of operations. They keep you moving and save you from costly mistakes.
Types of CNC Drilling Machines
| Sr. No. | Type of CNC Drilling Machine | Key Features | Benefits | Applications |
| 1 | Upright CNC Drill Press | Robust design, powerful motors, wide spindle speed range, vertical spindle orientation | Versatile, handles large workpieces, precise drilling, robust structure | Metal fabrication, woodworking, plastics, batch production, prototype development |
| 2 | Radial Arm CNC Drill Press | Movable radial arm, adjustable spindle positioning and angle, expansive reach | High flexibility, drills large/awkward parts, adjusts drilling angle | Large machinery construction, shipbuilding, large metal structures, custom drilling |
| 3 | Gang Drilling Machine | Multiple spindles on a single table, simultaneous drilling, independent or unison operation | High throughput, reduced production time, minimizes setups, consistent results | Automotive components, electronics, metal fabrication, aerospace and defense (high production rates) |
| 4 | Bench-top CNC Drill Press | Compact design, suitable for small to medium-sized workpieces, wide speed ranges | Space-saving, precise drilling for small operations, cost effective | Small parts manufacturing, prototyping, education, jewelry making, medical device manufacturing |
| 5 | Multiple Spindle Drilling Machine | Multiple independently operated and adjustable spindles, simultaneous hole creation | Increased productivity, minimized cycle times, efficient for large scale production. | Automotive, aerospace and mass production of parts with complex drilling patterns. |
| 6 | Turret-type CNC Drilling Machine | Rotating turret with multiple tools, automated tool changes, CNC controlled tool operations | Quick tool changes, increased efficiency, versatility for various operations, precise control | Electronics, metalworking, machinery fabrication, prototyping, custom manufacturing |
| 7 | CNC Deep Hole Drilling Machine | Specialized for deep holes, advanced chip removal and coolant systems, high straightness/precision | Deep hole accuracy, single operation deep drilling, minimizes deviation | Oil and gas, aerospace, medical equipment, hydraulic systems, barrel manufacturing |
Upright CNC Drill Press
Upright CNC drill machine is one of the most popular and commonly used drilling machine in an upright configuration. It is suitable for a great variety of drilling jobs with high precision.
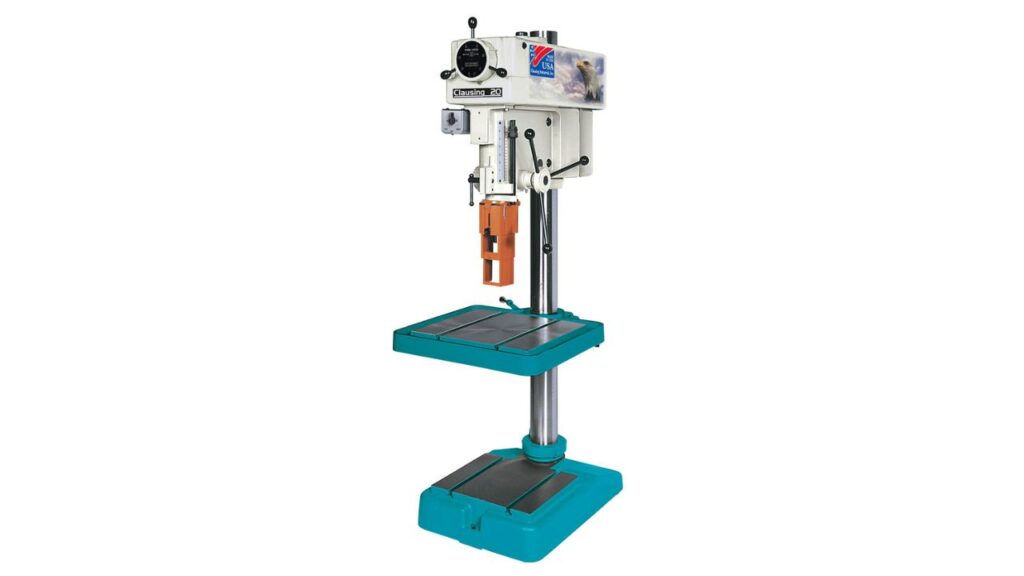

Features
- It has high spindle speed variation for different materials.
- It can work efficiently on both small and large workpieces.
- It is designed for accurate drilling patterns.
Benefits
- Accommodates different drilling operations.
- Suitable for high-precision applications.
- Handles various material thicknesses with ease.
Applications
- Used in metal fabrication, woodworking and plastics industries.
- Best for batch production, custom manufacturing, and prototyping.
Radial Arm CNC Drill Press
Radial arm CNC drill press is an angular drilling machine that incorporating movable arm that gives flexibility in drilling at different angles and positions. More versatile than upright drill presses, it adds up to versatility.
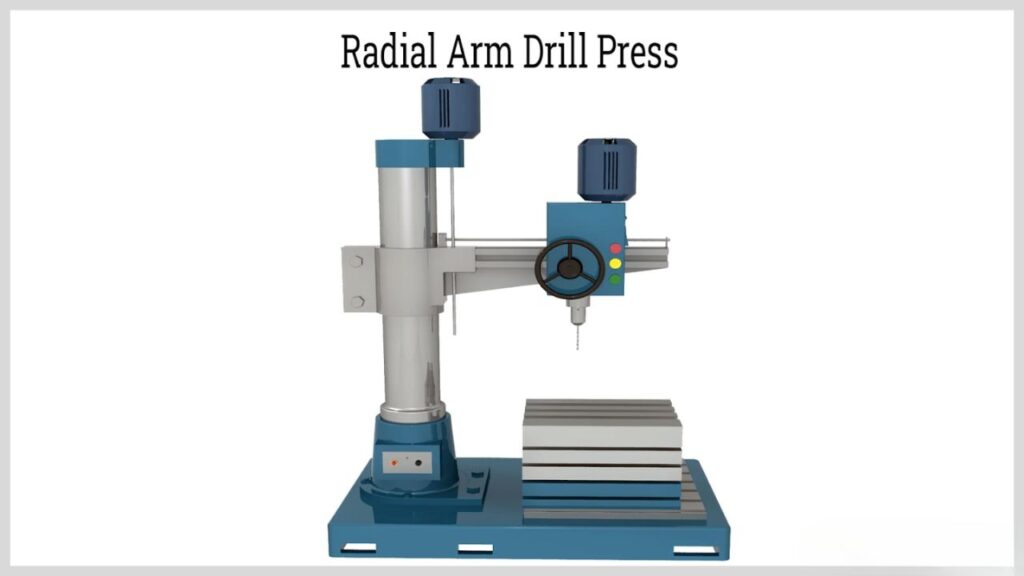

Features
- Drilling at non standard angles is possible with adjustable arm.
- It is suitable for drilling large and irregularly shaped workpieces.
- Greater reach than upright drill presses.
Benefits
- Increases flexibility in drilling operations.
- Handles larger workpieces without repositioning.
- Reduces the possibility of having to set up multiple times.
Applications
- Used in the construction of ships, heavy equipment and large metal structures.
- Perfect for applications where custom hole placement is needed.
Gang Drilling Machine
Multiple drill heads are mounted on a single table, with each drill head of drill machine CNC is capable of doing drill simultaneously.
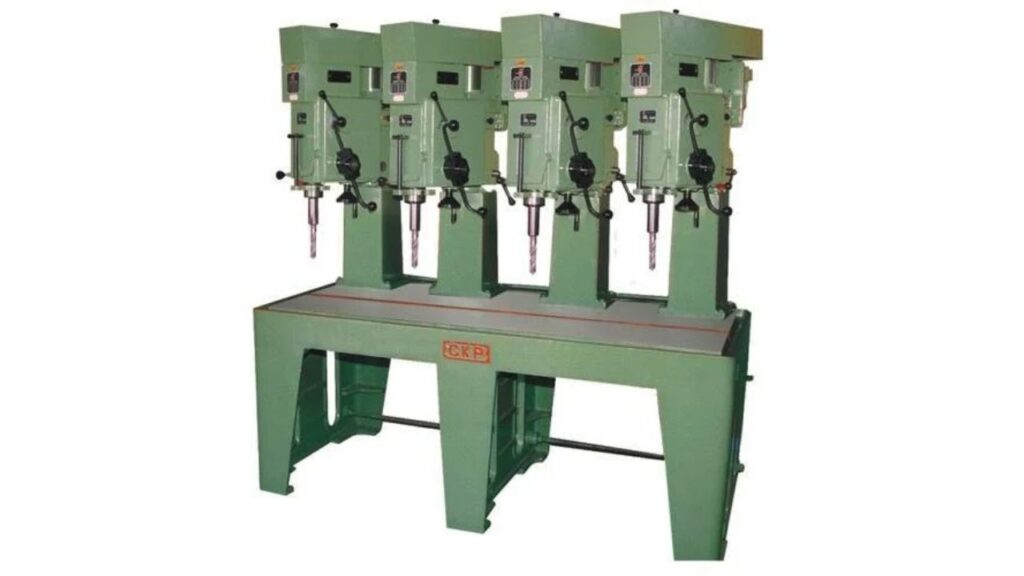

Features
- Multiple spindles perform simultaneous drilling.
- Drill in varying hole sizes in one pass.
- Customizable spindle configurations.
Benefits
- Increases production speed and efficiency.
- Eliminates errors from multiple setups.
- Enhances consistency across large batches.
Applications
- Common in automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing.
- Suitable for high-volume part production with multiple holes.
Bench-top CNC Drill Press
A bench top drill cnc press is a compact and space saving drilling machine meant for use in small scale operations that demands for high precision.
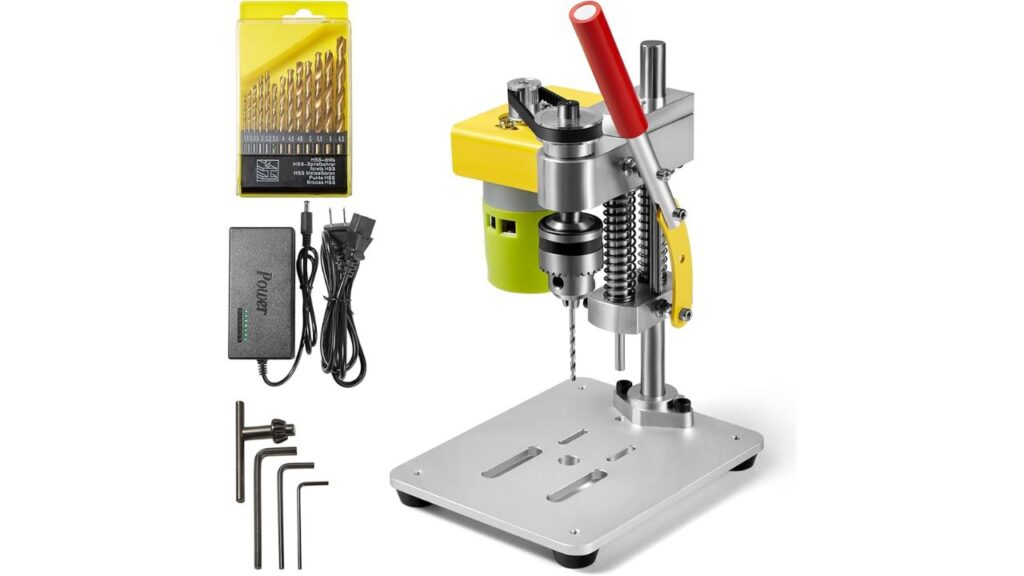

Features
- Smaller footprint, suitable for limited spaces.
- Drilling is fully controlled by a CNC machine to achieve the accuracy and repeatability.
- Handles a variety of materials.
Benefits
- Excellent for small scale production and prototyping.
- Lower cost than large CNC machines.
- Provides precision drilling in minimal space.
Applications
- Used in jewelry making, medical device manufacturing and educational labs.
- Prototyping and small parts manufacturing.
Multiple Spindle Drilling Machine
A multiple spindle drilling machine helps you work faster because each drill head operates independently.
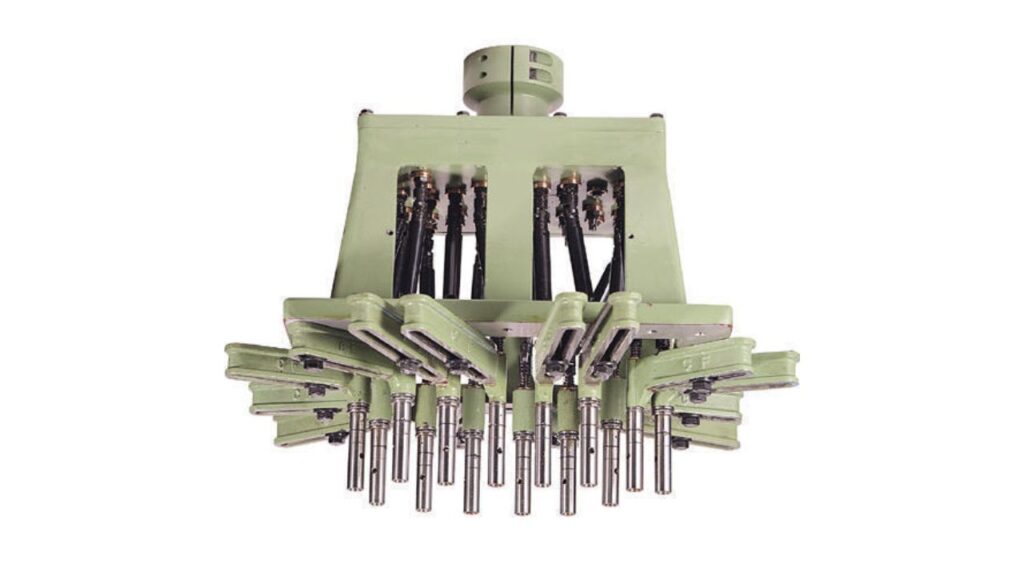

Features
- Adjustable spindles for different hole sizes.
- Customizable drilling patterns for specific needs.
- Significantly reduces drilling time.
Benefits
- Ideal for mass production.
- Ensures high consistency and precision.
- Reduces labor and setup time.
Applications
- These machines perform drilling tasks in automobile production facilities and military installations.
- Suitable for components with complex hole patterns.
Turret-type CNC Drilling Machine
An automated drilling machine with a turret can perform multiple drilling tasks quickly through fast drill tool exchanges.
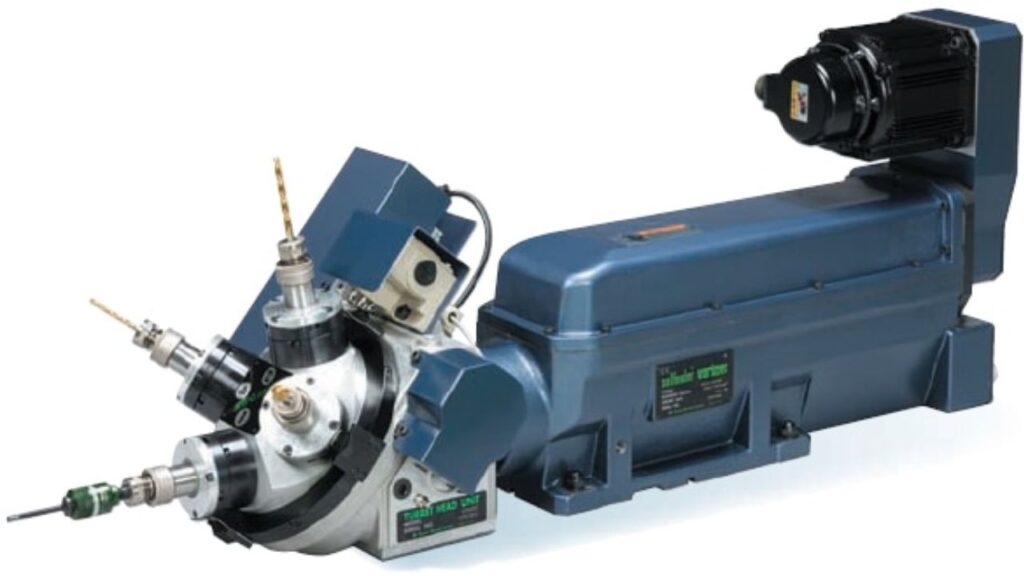

Features
- Automatic tool changer for seamless operation.
- Reduces downtime between drilling operations.
- Programmable CNC controls for efficient production.
Benefits
- Increases production speed and efficiency.
- The equipment performs many drilling tasks in sequence without someone needing to step in.
- Reduces errors and enhances consistency.
Applications
- This device works in electronics production and helps make high precision components for machines.
- This system provides the best solution for production lines that perform many different drilling tasks.
CNC Deep Hole Drilling Machine
This drill machine makes precise deep holes at high levels of accuracy and precision. CNC deep hole drilling machines exist to address specific manufacturing requirements in particular sectors.
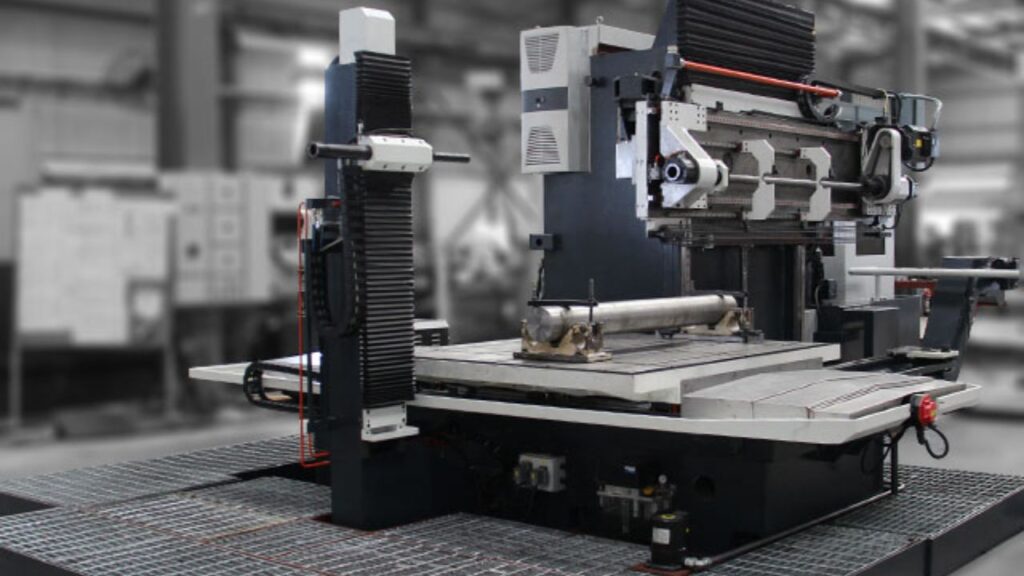

Features
- This technology utilizes extended drill tools and advanced cooling systems to operate.
- Our machine maintains tight hole alignment across all depth levels.
- This equipment helps maintain accurate depth control throughout deep drilling processes.
Benefits
- Enhances efficiency in deep-hole manufacturing.
- Drilling takes fewer steps thanks to this system.
- Our machine delivers exact part alignments to stay true to designed specifications.
Applications
- Essential in oil and gas, aerospace, and medical device industries.
- This equipment serves multiple uses including hydraulic and structural assemblies and barrel production.
Portable CNC Drilling Machine
A CNC drilling machine is a computer numerical control lathe that moves between different work locations, drills big parts in distant areas.
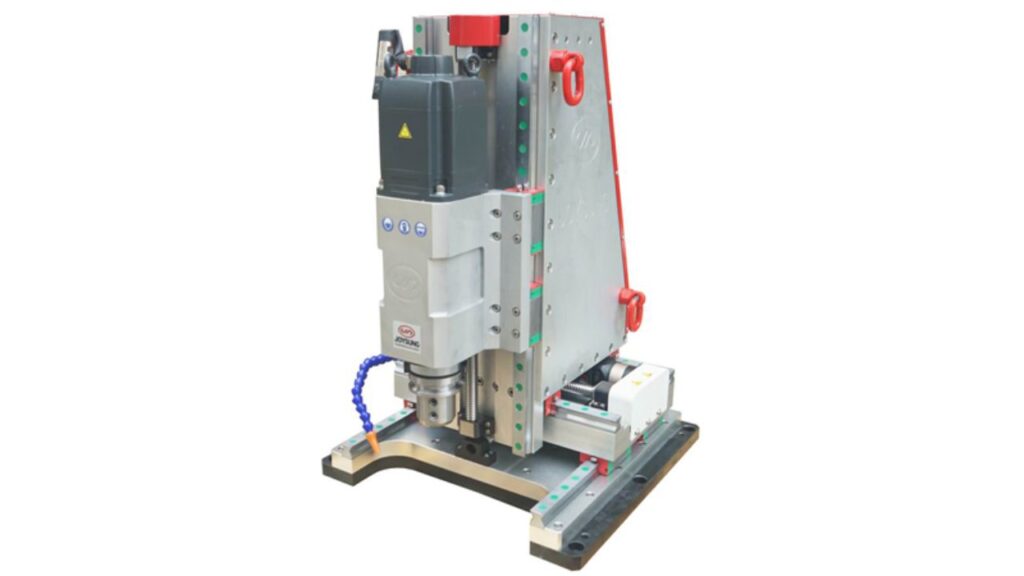

Features
- Compact and easy to transport.
- A CNC machine produces accurate drilling results thanks to its built-in programming control.
- The system installs directly onto drilling surfaces.
Benefits
- The portable The computerized drill machine gives exact results at distant job sites.
- The device helps us avoid moving big parts from one place to another.
- Ideal for fieldwork and maintenance operations.
Applications
- People use this tool for building ships and construction work plus maintaining heavy industrial equipment.
- Suitable for infrastructure projects and repair operations.
What Are the Different Types of CNC Drill Bits?
Selecting the correct CNC drill bit is critical to precision and efficiency of machining. Each type is designed with a specific purpose and each hole created in each material. This understanding will help you get better results. The following are the main types of CNC drill bits:
Twist Drills:
Twist drills are helical drill bits, used for chip removal and are the most common. General purpose drilling in materials such as metal, wood and plastic is well suited to this type of drill. These bits come in high speed steel, cobalt, and carbide, and are very durable and versatile.
Center Drills:
These short, stiff drill bits make starter holes for accurate positioning. This rigid design helps prevent wandering and their use is essential for accurate hole alignment in machining operations. Typically used before larger drills to ensure stability.
Spot Drills:
Shallow dimples produced by spot drills guide twist drills and prevent them from drifting. Their wider point angle allows the main drill to start exactly where needed. They are usually used in high precision applications.
Peck Drills:
Peck drills are designed for deep hole drilling and work in increments to improve chip evacuation. This method eliminates heat buildup and protects the tool from damage. For hard materials with lots of heat and resistance in drilling, it is ideal.
Carbide Drills:
Solid carbide bits for these bits offer exceptional hardness for high-speed drilling. For tougher materials like hardened steel, composites and ceramics, they are best suited. Longer tool life and precise cutting are ensured by their wear resistance.
Indexable Drills:
These drills use replaceable cutting inserts, as opposed to the solid edge. They are very cost effective for high production machining given this design. You can replace the insert when it wears out without changing the whole drill bit.
Coolant-fed Drills:
The internal coolant channels of these bits deliver fluid directly to the cutting area. Coolant reduces heat, improves chip evacuation and extends tool life. Deep and high speed drilling applications use them.
Step Drills:
Multiple cutting diameters on a step drill lets you drill different hole sizes with the one bit. They are commonly used in sheet metal work for clean, burr free holes with no need of multiple drill bits.
What Are the Main Parameters of CNC Drilling?
However, the success of CNC drilling depends on controlling key parameters that relate to precision, efficiency and tool life. Knowing these factors allows you to drill at peak performance while delivering high quality results. Let’s break down the main computer controlled drilling parameters and what they do in machining.
Spindle Speed (RPM):
The revolution per minute (RPM) is the rate at which the drill bit rotates. Speed will depend on the drill bit and material type. To prevent overheating and tool wear, harder materials require lower RPMs, while softer materials require higher RPMs for cleaner cuts.
Feed Rate (mm/min or in/min):
This is the speed at which the drill bit moves into the material as measured in millimeters or inches per minute. Balance feed rate to avoid excessive wear or bit break away. Rough holes can be caused by a feed rate that is too fast, and overheating and poor efficiency can result from a feed rate that is too slow.
Cutting Speed (SFM or m/min):
This is the speed with which the cutting edge moves through the material. At a given spindle speed and drill diameter, however, it depends. The cutting speed used should be proper to achieve smooth finishes and maximize tool life. Overheating, high friction, and poor hole quality can result from incorrect speeds.
Depth of Cut:
This is what controls how deep the drill bit cuts in each pass. Your depth should be adjusted for chip evacuation needs and material properties. Peck drilling (removing material in stages) is used in deep-hole drilling to prevent overheating and increases accuracy.
Tool Material and Geometry:
Performance is affected by the material and design of the drill bit. Common choices are high speed steel (HSS) and carbide bits. Drilling efficiency, chip removal, and hole precision are all influenced by the point angle and flute design.
Coolant and Lubrication:
Proper cooling in machining centres for drilling helps prevent heat buildup and reduces friction while improving tool life. According to the material and drilling method you can use liquid coolants or mist lubrication. Cooling also efficiently removes chips and enhances surface finish.
What Are the Supported Materials in CNC Drilling?
CNC drilling machines are available that can handle different materials and each material will require specific tools and settings to give you the best end result. This knowledge helps you to be precise and efficient with manufacturing.
Metals
You can drill aluminum, stainless steel, brass, copper, titanium. With strength and durability, these metals are perfect for industrial use. Hole placement for parts in aerospace, automotive, and machinery industries is ensured by accuracy of hole placement through CNC drilling.
Plastics
Plastics that are commonly drilled include acrylic, polycarbonate, ABS, nylon, PVC, and PTFE (Teflon). The materials give us lightweight, corrosion resistance, and flexibility. Automated drilling enables you to make fine holes in electronic enclosures, medical devices and automotive components.
Composites
Two popular composite materials are carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP) and fiberglass. Their high strength to weight ratio benefits you. Carefully controlled CNC drilling contributes to negligible delamination as well as clean, precise holes.
Wood
Automated drilling system is widely used with hardwoods like oak and maple, softwoods like pine and cedar, and plywood and MDF. With precise cuts and smooth finishes, you can easily make furniture, construction components and decorative designs.
What Are the Applications of CNC Drilling?
In modern manufacturing, precision and efficiency are delivered by programable drilling machines This helps standardize the hole creation method for structural integrity and functionality. Automated drilling techniques are applied to many industrial sectors described below.
Aerospace
Aircraft components require precise drilling. Fasteners, wiring, and airflow are created through holes in materials such as titanium and composites using CNC drilling. Meeting safety standards requires high accuracy.
Automotive
Computerized drilling system can be used to manufacture engine parts, chassis and structural parts. It helps ensure that fasteners achieve exact hole placement, reducing vehicle durability and performance issues.
Manufacturing & Machinery
You rely on CNC drilling to manufacture machinery parts and industrial tools. This guarantees precision so that components are fitting perfectly and running simultaneously on varying machines.
Electronics
Automated drilling in electronics creates precise holes in circuit board and enclosures. This helps with proper mounting, cooling and connectivity in compact electronic devices.
Medical
Producing surgical instruments and implants requires precision drilling. As a medical tool, CNC drilling meets the most strict standards.
Construction & Architecture
CNC drilling is a part of creating structural components for buildings or bridges. It makes certain strong and durable connections that provide the durability in construction projects.
Energy Sector
CNC drilling is used to manufacture components for turbines, pipelines and energy infrastructure. The safety and efficiency of energy systems require precision.
Furniture
Furniture making uses CNC drilling to fasten and dowel. This enables a consistent, high-quality production of wooden and composite furniture.
Musical Instruments
Acoustic component fabrication depends on precision drilling. CNC drilling provides accurate hole placement to preserve the quality of musical instruments.
Research & Development
CNC drilling helps in prototyping or experimental creation of parts. It provides you with the means to test designs with accuracy in a multitude of industries, supporting innovation.
What Are the Advantages of the CNC Drilling Process?
CNC drilling is an unparalleled form of precision, efficiency, and versatility found in modern manufacturing. Your CNC provides you with consistent, high quality results. The key advantages of CNC drilling are as follows:
High Precision and Accuracy: Holes are placed and dimensioned exactly with CNC drill machine within ±0.005 inches (±0.127 mm). It gives you precise numbers every time, reducing errors and rework.
Efficiency and Speed: Drilling is much faster using a CNC machine than using manual methods. The ability to produce high volumes of parts quickly reduces production time and raises the output.
Versatility: CNC drilling is used to drill through various materials such as metals, plastics and composites. It can be used across many industries, such as aerospace, automotive, etc.
Automation and Consistency: CNC drilling reduces errors that can occur due to human error. This gives you results that are uniform in every batch, thereby good reliability.
Cost-effectiveness: CNC drilling can help you reduce material waste and labor costs which helps optimize the production expenses with quality.
Compatibility with Other CNC Processes: CNC drilling can be integrated with milling, tapping, and computer numerical control lathe operations that allow your workflow to be more efficient and seamless.
Does CNC Drilling Have Any Limitations?
Although automated drilling is an efficient process, it has limitations. These help you to make informed decisions when manufacturing.
- High Initial Cost: Machines and setup require a heavy investment. It can be a difficult thing for small businesses.
- Limited to Round Holes: Without extra machining steps, you can’t create non circular holes.
- Material Constraints: Certain brittle materials are prone to damage unless handled in a certain way.
- Setup and Programming Time: But it requires time spent programming and skilled operators for precision.
Is CNC Drilling Cost-Effective?
CNC drilling is precise and efficient, but is cost effective based on several variables. The initial investment may be high, but in the long run, it is a cost effective option.
Factors Affecting Cost
- Machine Cost: CNC machines with higher upfront price but better accuracy and durability reduces the long term expenses.
- Material Costs: Costs increase with harder materials due to stronger drill bits and longer processing times. Drilling softer materials is easier and cheaper.
- Tooling Expenses: First cost is higher for high end drill bits and cutting tools, but they will last longer, cutting down on the need to replace frequently and the down time associated with it.
- Labor Costs: CNC drilling reduces manual intervention to lower labor costs and improve throughput. However, skilled operators can still add to expenses.
Long-Term Savings
- Reduced Rework: The CNC drilling provides the most precise cuts with the least amount of material waste and rework costs.
- Lower Scrap Rates: Reduction of errors from accurate drilling means that raw materials are saved and total cost is lower.
- Optimized Labor Efficiency: If the processes can be automated, fewer people will be needed and so labor costs will fall over time.
High-Volume Production
- Economies of Scale: As setup expenses are spread out across more parts the per unit costs are lowered.
- Faster Turnaround: Bulk orders are completed sooner with CNC drilling, increasing profitability and enabling the meeting of demand.
- Consistent Quality: Uniform quality is possible at high volume production in order to maintain a very high degree of consistency.
How Long Does CNC Drilling Typically Take?
CNC drilling needs different times depending on several elements. A single hole may take seconds or minutes. The time spent on a basic aluminum drilling task takes seconds while a difficult steel or titanium process may need multiple minutes to complete one hole using a drill cnc system. The finish time relies on multiple influencing elements.
- Drilling tools experience excessive wear when they cut through hard materials at fast speeds.
- Precise drilling of deep and large holes demands additional time for proper drilling techniques and chip management.
- Modern CNC systems finish drilling operations faster than basic machines with lower performance.
- Having to switch between different drill bit sizes lengthens the total process time.
- An operator who knows the system can set parameters that shorten cutting time without losing precision.
Using advanced drills at top speed allows you to pick ideal tool paths and drill deep holes via peck drilling methods.
What Are Important Considerations for Effective CNC Drilling?
Several key elements must be taken into account to achieve precise and productive CNC drilling outcomes.
- Proper Tool Selection: Pick a drill bit that fits your material strength and choose the proper size for your intended hole depth. Carbide drills handle durable materials best and HSS tools deliver great results when working with malleable materials.
- Optimal Drilling Parameters: Adjust your drill machine settings based on the material properties and drill bit specifications. Running a drill engine at high speeds generates excessive heat which reduces its performance and low-speed operations result in subpar results.
- Chip Evacuation: Good chip removal extends tool lifetime and produces precise holes in the workpiece. Special coolant systems with peck drilling methods efficiently remove chips from deep holes.
- Tool Wear Monitoring: Regularly inspect your drill bits and switch them out when their condition starts to degrade hole precision. Tools that show signs of wear compromise their ability to produce smooth dimensions when drilling operations.
- Use of Coolant and Lubrication: Coolants keep the temperature from rising which extends tool lifespan and gives better surface finishes.
- Efficient Workpiece Clamping: Tighten the material to block vibrations that decrease drilling precision.
Good control over these variables lets you make better drilling results while keeping your operations running smoothly.
Conclusion
Controlled drilling machines help CNC manufacturing create exact drilling results. You achieve better drilling outcomes by managing both tool speed and fluid usage effectively. This system gives small parts at reasonable rates but creates imprecise results with deeper drilling. Companies across aerospace defense medical automotive sectors rely on high precision CNC drilling machine to create perfect holes in their
FAQs
What Is the Difference Between Drilling and Thread Tapping?
A self-operating tool spins to create round holes that accept fasteners. Thread tapping inserts threads inside holes using a tap tool to make smooth bolt or screw connections. The drilling phase defines the work area while the thread tapping process installs threaded fasteners.
What Is the Difference Between CNC Milling and Drilling?
The CNC machine creates straight holes by moving its rotating drill bit up and down along the Z-axis. A CNC milling machine creates precise 3D parts by moving spinning cutting tools across multiple directions. Our CNC machines do slotting and contour work as well as engraving tasks.
What Is the Difference Between CNC Drilling and a CNC Lathe?
The drilling machine clamps the part in place as a spinning drill moves right through it. The CNC lathe tool stays fixed in its position while working on turning rotating parts. Drilling tools create holes yet lathes transform material into round shapes by facing turning and thread processing methods.
What Is the Maximum Hole Depth Achievable with Computer-Controlled Drilling?
A typical drilling tool can punch its way through materials that are more than ten times thicker than itself. Specialized drilling CNC machines with peck tools and coolant systems produce deeper holes by controlling heat and managing waste efficiently. Manufacturers use advanced drilling methods to produce deep holes in medical tools aerospace components and automotive spindles.
