CNC Mill and Turn 101 – Everything You Need to Know
Manufacturing today depends heavily on CNC Mill and Turn machines for their accuracy and speed. If you handle complex pieces or seek to speed up your production process, it’s very important to understand this technology. When you understand how CNC mill-turn works, it’s easier to pick the best machine, increase your output and cut costs. You’ll learn in this guide what CNC mill-turn is, how it operates and what sets it apart from other types of manufacturing machines. You’ll learn about important features, different types, advantages and other aspects so that you can make better choices in machining and stay ahead of your competitors.
Table of Contents
ToggleCNC Mill and Turn: Definition and Core Concept
The use of a CNC mill-turn machine means you can perform both milling and turning in a single setup, resulting in quick and precise work on difficult parts. The workpiece is turned by a rotating spindle as live tools mill the part. Main and sub-spindles, tool turrets and live tooling systems combine to manage several operations without the need for repositioning.
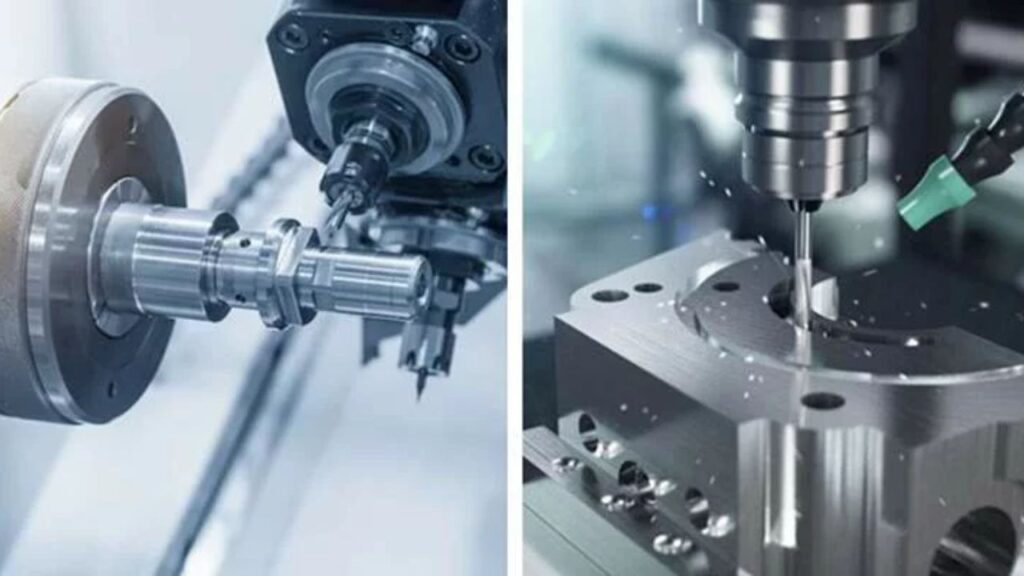

How CNC Mill and Turn Machines Work
CNC Mill & Turn machines use a single setup to do both turning and milling at the same time. You begin by rotating the workpiece on the primary spindle so you can do turning operations. After that, the next step involves using live tools or secondary spindles to mill the part without removing it. All movements and operations of the tools are matched by the machine for accurate results. You use advanced CAM software to plan the toolpath which helps your machine move efficiently and finishes the job in less time. Machining is made easier as coolant removes heat and reduces wear. By clearing the chip area, the systems allow you to maintain precision and get the most out of your tools each time.
Key Components of CNC Mill Turn Machines
| Sr. No. | Component | Function |
| 1 | Main Spindle | Rotates the workpiece for turning operations |
| 2 | Milling Head | Houses tools for cutting operations |
| 3 | Tool Turret/ATC | Automatically changes tools during machining |
| 4 | Sub-Spindle (if any) | Allows secondary operations without repositioning |
| 5 | Axis Drives | Provides motion to different axes (X, Y, Z, B, C) |
| 6 | Control System | Brain of the machine (Fanuc, Siemens, etc.) |
Types of CNC Mill-Turn Machines
Horizontal Mill-Turn Centers
Horizontal mill-turn centers are designed so that the spindle runs horizontally. It is best used for long, cylindrical items such as shafts and rollers. Gravity aids in clearing the chips, increasing how clearly you can see the cut and keeping things cooler. The strong and stiff frame makes these machines less likely to move when you are making heavy cuts. If your parts have close tolerances and are complex, horizontal machines provide great results but occupy more floor space.
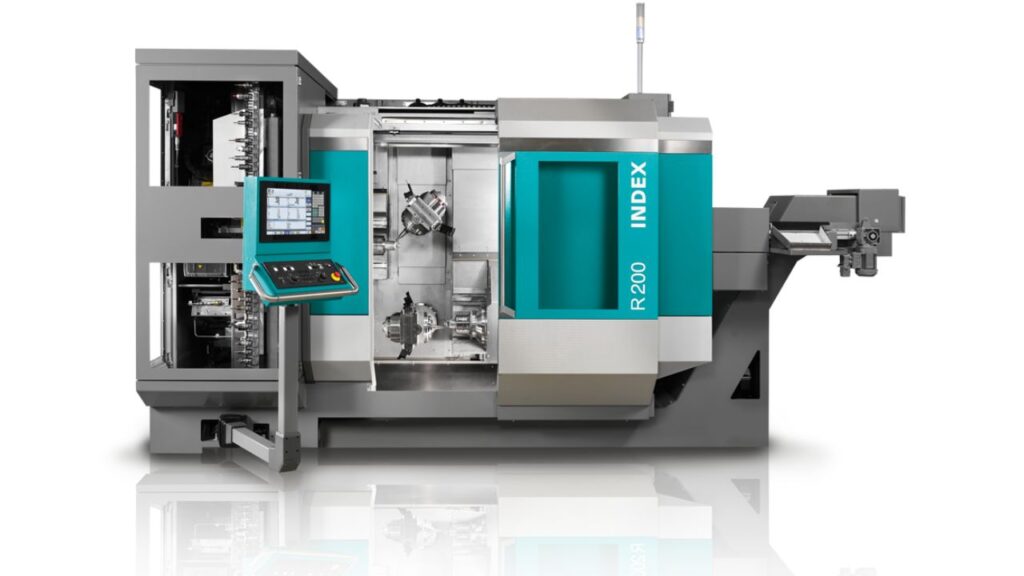

Vertical Mill-Turn Centers
Vertical mill-turn machines have the spindle standing vertically. Because of this design, you can more easily lift and place heavy or wide workpieces like discs, wheels or rings. Because they take up less space, they’re ideal if your workshop is small. Vertical setups make it much easier to use clamps and keep the work aligned. On the other hand, they aren’t well-suited for parts that are too long, so you might not be able to use them for some projects.
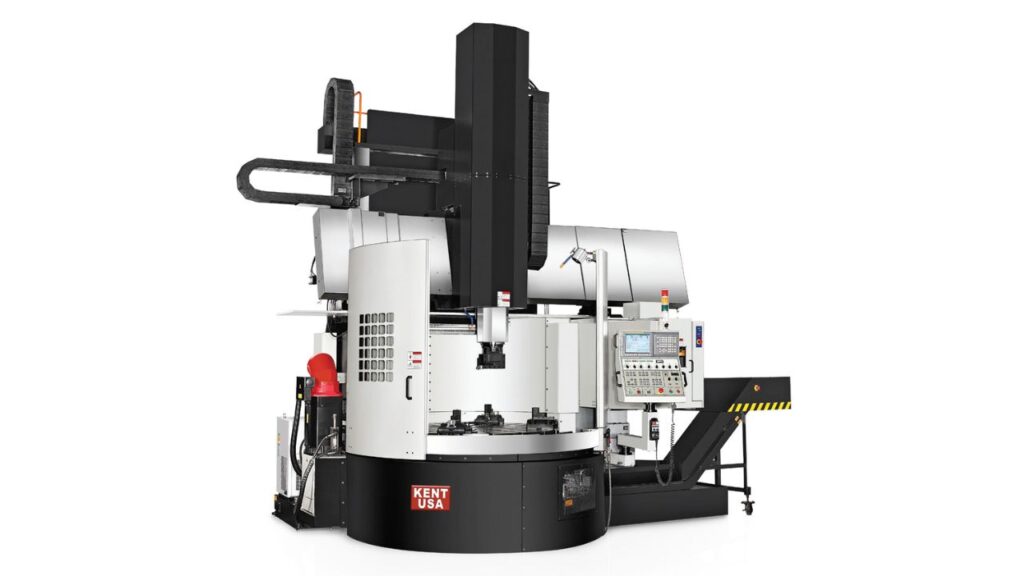

Multi-Turret Mill-Turn Machines
You can carry out multiple operations at the same time with multi-turret systems. You can use various tools at the same time which decreases cycle time a lot. If you need to machine parts that have high volumes or several features, it grants you more flexibility and helps you complete more parts. You can use specific tools over a longer period which saves time.
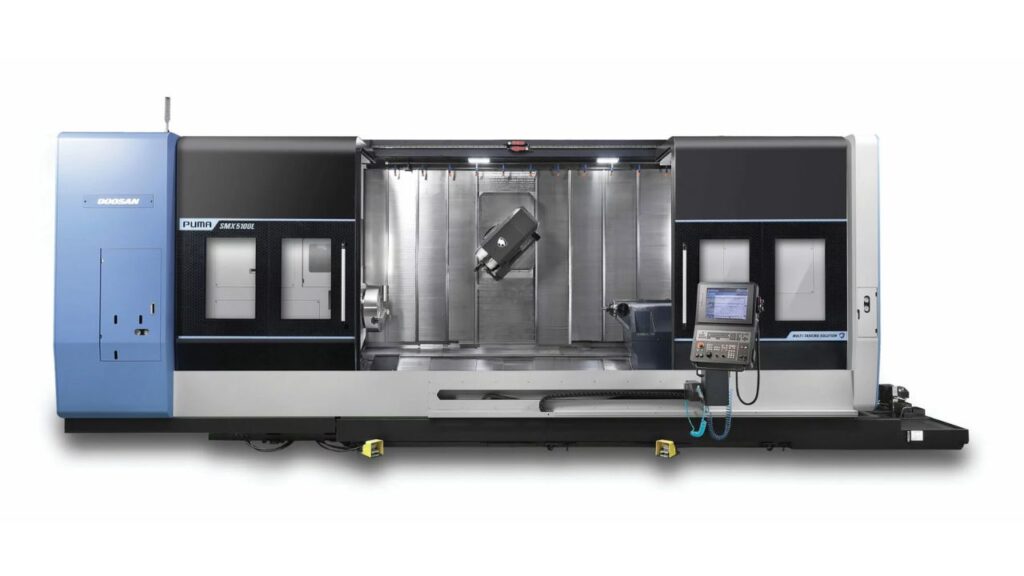

Twin-Spindle and Multi-Spindle Configurations
You can do secondary operations on twin-spindle or multi-spindle machines without taking the part off or putting it back on the machine. This way, you can machine both the start and the finish of a part at one time. They are designed to assist advanced automation. If you seek to handle parts better, increase precision and use lights-out machining, this is the setup to consider.
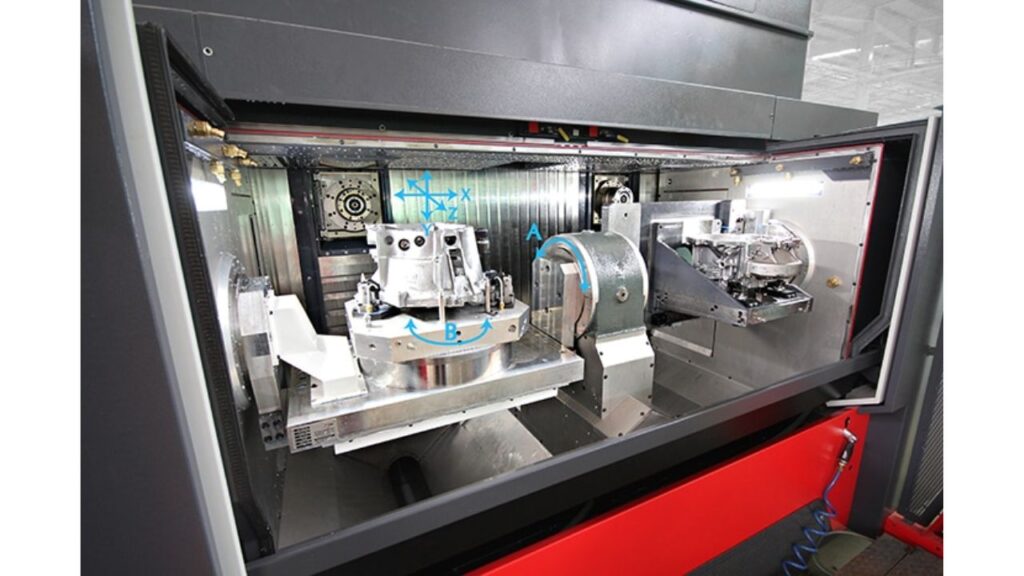

| Type | Axis Layout | Ideal For | Pros | Limitations |
| Horizontal Mill-Turn | Horizontal | Complex shafts, long parts | High rigidity, gravity-aided chip removal | Space-consuming |
| Vertical Mill-Turn | Vertical | Discs, round components | Small footprint, easy setup | Limited for long parts |
| Multi-Turret | Variable | High-volume, multi-feature parts | Parallel operations, reduced cycle time | Complex programming |
| Twin-Spindle | Horizontal | Front and back operations | Automation-ready, flexible | Higher upfront cost |
Advantages of CNC Mill Turn Technology
Increased Accuracy and Precision
CNC mill-turn machines help you produce tight tolerances and repeatable quality results. Combining milling and turning in one machine reduces errors caused by misalignment. You can always get the same results in each batch, making it important for high-precision industries.
Reduced Setups and Cycle Time
One run on a mill-turn machine performs several different operations. There is no need to transfer components from one machine to another. This shortens the time you spend setting up and increases your speed of manufacturing. There is no drop in quality, but you save a great deal of time.
Lower Tooling and Fixturing Cost
You require fewer special tools and fewer fixtures since everything stays on the same machine. Changes to tools are done without human involvement and with speed. As time goes by, you’ll find that you spend less on tools and fixtures.
Higher Productivity with Complex Parts
With CNC, you have the ability to perform complex cuts in only one pass. It is perfect for when you have to perform rotational and milling operations on the same part. You are able to make more output without hiring more workers.
Compact Machine Footprint
Mill-turn machines merge two systems into one machine. This allows you to save room on your shop’s floor. You increase efficiency and use your facility better.
Superior Surface Finish and Tight Tolerance
With a stable setup and exact control, you produce smoother finishes on your parts. Your need for secondary operations is lessened. By using this approach, you can make sure your components fulfill strict requirements with almost no extra effort.
Comparison: CNC Milling vs Turning vs Mill-Turn
| Feature/Aspect | CNC Milling | CNC Turning | CNC Mill-Turn |
| Machining Type | Subtractive | Rotational Cutting | Hybrid |
| Number of Setups | Often Multiple | One or Two | Usually One |
| Complexity Handling | Medium to High | Low to Medium | High |
| Flexibility | Good | Moderate | Excellent |
| Machine Cost | Lower | Lower | Higher |
Common Applications of CNC Mill & Turn
Aerospace Components
Precision is an absolute requirement in the field of aerospace. CNC mill-turn machines help you create turbine shafts and engine housings that have precision and a smooth finish. One setup can create complex shapes, making errors less likely and giving all parts the same quality.
Automotive Parts
For the automotive industry, the use of CNC mill-turn equipment allows you to handle the production of transmission shafts and brake parts easily. You will be able to produce more and still keep your results correct which is crucial for safety-critical systems.
Medical Devices
Medical tools and implants must be produced with great accuracy. With mill-turn machines, you are able to manufacture surgical instruments and orthopedic implants with close tolerances. You make sure that all batches are made the same way which is crucial for complying with tough rules.
Energy Sector
In energy applications, it is important that sensors are both durable and accurate. With CNC mill-turn machines, you can manufacture valve bodies and pump parts that can handle tough conditions. By machining complex shapes, you don’t need to keep repositioning the part.
General Precision Engineering
For those in general engineering, CNC mill-turn machines are truly flexible. Since you can build complex geometries in one go, you will save time and enhance your productivity. For when you want to produce small batches or parts that need to be exact, this is your best choice.
Tooling in CNC Mill-Turn Machines
Making the most of your CNC mill-turn machine depends on having the right tooling. Let’s look at the tooling systems that help achieve better results and higher precision.
Live Tooling Systems
Live tooling means you can mill, drill or tap a part without having to take it off the tooling system. Because tools can be rotated individually, it becomes simpler to make complicated parts in a single setup.
Turret-Mounted Tool Holders
They make it easy to store and access your tools. It is easy to change between turning and milling tools, allowing you to work more flexibly and spend less time not doing anything.

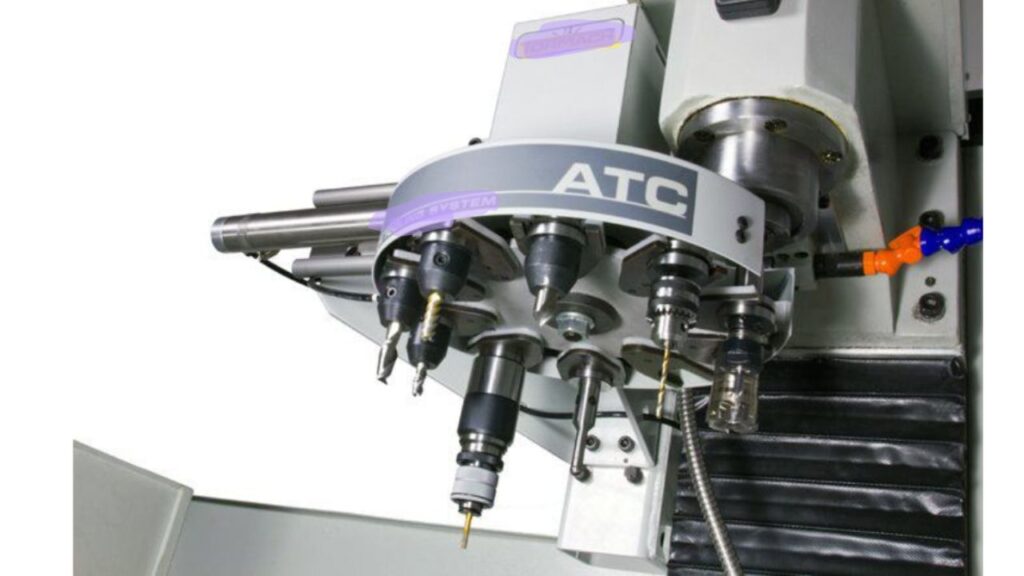
Automatic Tool Changers (ATC)
In the middle of a process, ATCs switch tools for you, speeding up your work. Since you don’t have to pause the machine, work becomes more efficient and you can easily manage various tasks.

Coolant-Through-Tool Systems
The coolant is delivered from the system straight to the part being cut. You’ll see improved temperature regulation, longer tool life and a better surface finish.

Tool Wear Monitoring and Adaptive Control
It allows you to observe tool wear immediately. Setting cutting conditions automatically helps you create parts with less waste and better quality.
Challenges and Limitations
High Initial Investment
Buying a CNC mill-turn machine means you should expect a large initial expense. Because they do many things, these machines are generally more costly than simple one-purpose tools. Still, over time, this investment helps make operations more efficient and cut down on the number of times a machine needs to be re-arranged.
Complex Programming Required
It is not easy to program a mill-turn machine. It is important to be skilled in G-code and CAM software because you will perform both milling and turning operations. It’s natural to expect a slight learning period when you start using a milling machine.
Skilled Operator Demand
Your CNC mill-turn will perform best when it is controlled by skilled operators. Machines of this type must be installed carefully, watched carefully and fixed when necessary. It is important to either train your existing staff or bring in experts to keep the business on track.
Managing Tool Wear
When a machine is used for many operations, tool wear happens more quickly. Always make sure to inspect and change your tools so you don’t make mistakes or get poor results. Taking action in advance helps you stay on top of production.
Maintenance Complexity
There are many moving systems and parts found in mill-turn machines. It is important to make sure your machine is regularly checked and problems are resolved fast. Maintaining the machine as recommended will keep it working and help you avoid expensive repairs.
How to Choose the Right CNC Mill Turn Machine
Consider Part Complexity and Volume
The first step is to consider the difficulty of the parts and how many of them will be produced. Machines need to be advanced to handle complex parts with several features. Select machines that can work faster and automate many tasks for high-volume runs.
Machine Accuracy and Tolerances
When very tight tolerances are used, accuracy takes on greater importance. You want a machine that always meets your requirements for quality. Look at the machine’s precision ratings and confirm they are suitable for your parts.
Axes and Configuration
Pay attention to the configuration and the number of axes in the machine. The more axes a machine has, the more complex tasks it can handle. Be certain that the machine is arranged to meet the specific needs of your parts.
Material Compatibility
Check that the machine is compatible with your material of choice. Various types of machines are best suited to work with different types of metals. When you match the machine with the right material, it becomes more efficient and tool life improves.
Software & Control Compatibility
Choose a machine that has software and control systems that work well with your tools. A simple interface and trustworthy CAM software will help you program your machine more easily and reliably.
After-Sales Support and Training
It’s also important to look at what kind of support and training the manufacturer provides. Having good after-sales support gives you assistance anytime you need it and keeps your team knowledgeable, making your machine work at its highest efficiency.
Programming and Software in CNC Mill Turn
G-code Basics for Mill-Turn
It’s important to realize that programming for mill-turn involves both milling and turning commands. As a result, your G-code can manage more than one spindle and toolpath. If synchronization is done properly, collisions can be avoided and everything runs smoothly. While editing G-code, you work to ensure the tool and spindle move together for exact machining.
CAM Software Tools
You have options such as Mastercam, Fusion 360, Siemens NX or HyperMill as advanced CAM software. They make it simple to write multi-axis programs. They include software that converts your files into code for machines and lets you simulate multi-axis activity to find mistakes early.
Toolpath Optimization
Making toolpaths efficient decreases the number of tool changes and lowers idle time. Controlling your cutting tools and their feed rate improves how much work you finish and the life of your tools. If you optimize well, your manufacturing process will be smoother and faster.
Best Practices for Precision Mill-Turn Machining
Material Prep and Fixturing
The first step is to prepare your course material well. Use proper fixing to prevent the part from moving as you machine it. As a result, your measurements will not fluctuate and will be more accurate.
Proper Tool Selection and Holder Maintenance
Pick tools that are right for the work you are doing. Take care of your tool holders, as this will ensure they keep your tools steady. This way, your cuts are accurate and your tools last longer.
Vibration and Chatter Minimization
Vibration can be controlled by changing cutting speeds, feeds and the paths followed by the tool. If you notice that your shots are not stable, use dampeners or stabilizers. Reducing noise on the machine makes the surface smoother and protects tools and parts.
Cutting Fluid Optimization
Let the cutting fluid reduce heat on the tools and remove chips from the cutting area. Using the right fluid amount helps lower heat and friction which keeps your tools and parts in top shape.
Consistent Calibration and Probing
Remember to calibrate the machine and test measurements with probing. That way, your assembly is precise and all parts are within the correct specifications.
Monitoring Tool Wear and Proactive Replacement
Look for the signs that the tool is starting to wear out. Update your tools before they stop working so that you can produce quality results. Being proactive helps you save time and keeps the production process running smoothly.
Cost Factors and ROI Consideration
| Sr. No. | Factor | Impact on Cost/ROI |
| 1 | Machine Purchase Price | High upfront but long-term saving |
| 2 | Setup Time | Reduced significantly in mill-turn systems |
| 3 | Tooling Cost | Can be optimized with proper planning |
| 4 | Labor Skill Requirement | Higher, but increases output quality |
| 5 | Downtime & Maintenance | Must be minimized through predictive plans |
| 6 | Production Volume | Higher volumes make investment more viable |
Conclusion
CNC mill-turn machines have transformed the way modern manufacturing works by allowing both milling and turning to be done at the same time. As a result, this hybrid system offers superior accuracy, shorter lead times and less need for special tooling which makes it perfect for producing complex parts in aerospace, automotive, medical and energy industries. You should consider how complex your parts are, how much you need to produce and what material you will use before picking a machine and skilled programming and regular maintenance guarantee it works well. When you use CNC mill-turn technology, you achieve greater productivity, better surfaces and remain competitive in the current industry. Choosing the right machines helps your operation stay successful and adapt to changes over the years.
