What is CNC Quality Control?
CNC quality control is used to maintain parts to the required standards. It is a methodological process that oversees production procedures. Quality control encompasses all the stages, including the raw materials, up to the finished products. It is checking, testing, and remedial action. CNC quality control minimizes defects, enhances reliability and minimizes production errors. Components fit and work well in assemblies through proper control. It is also in line with global standards like the ISO and TS16949. We have strong quality control measures at CNCSwissMasion. Every component is checked strictly before exiting the factory. This will ensure high accuracy and satisfaction of the customer.
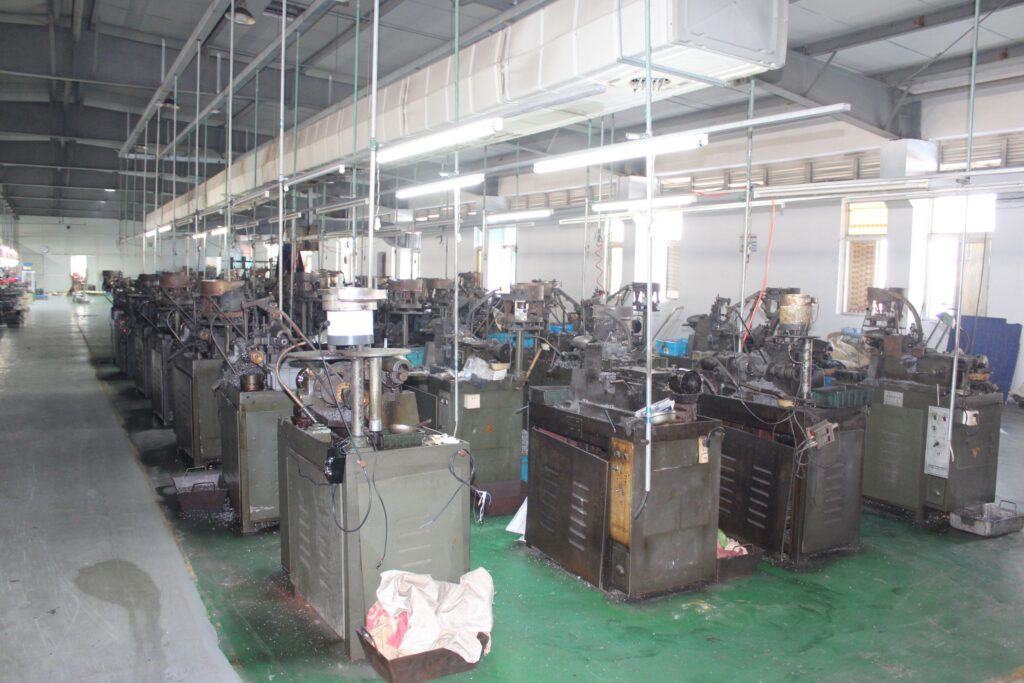
Our Advanced Machines for CNC Manufacturing
The quality of CNC machining depends on advanced machines. The CNCSwissMasion employs the high-precision equipment to make sure there is uniformity in accuracy. Our machines consist of Swiss CNC lathes, multi-axis mills and automated machines.
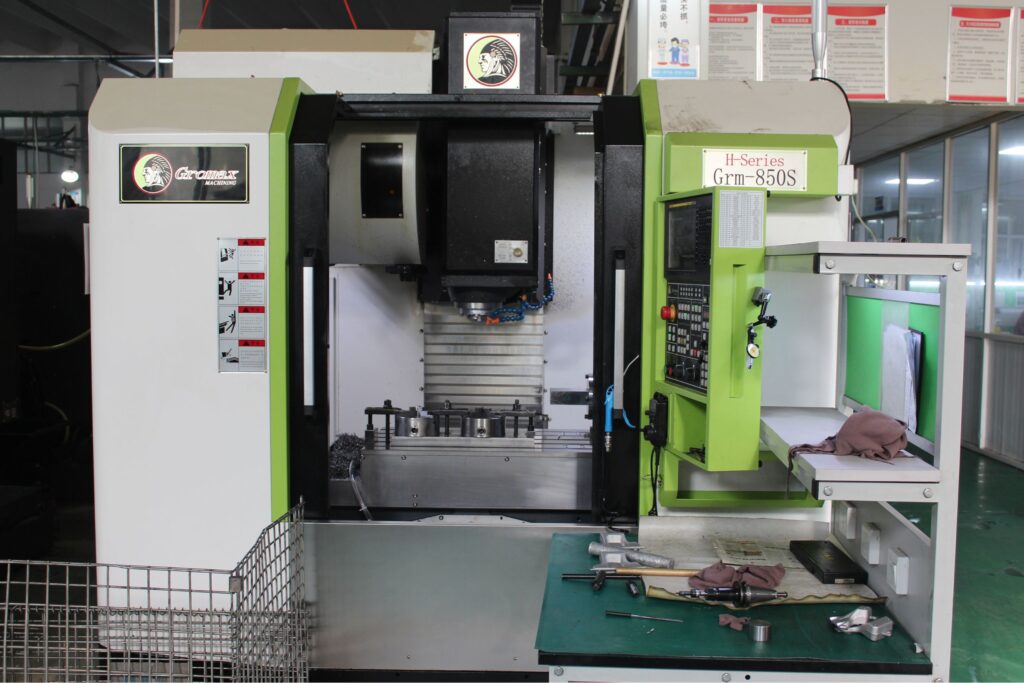
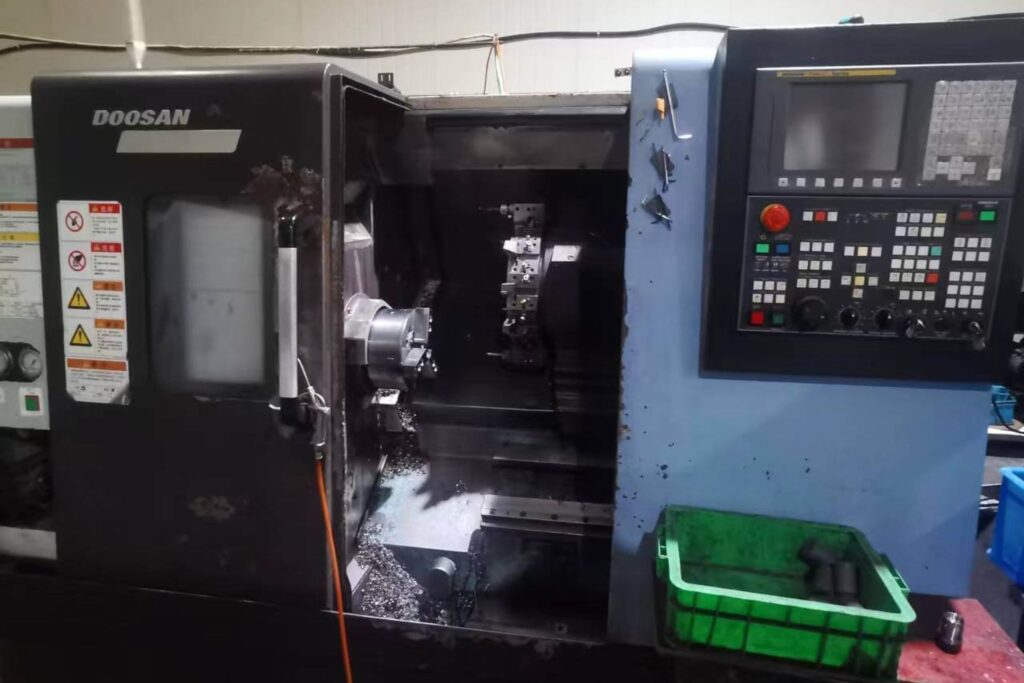
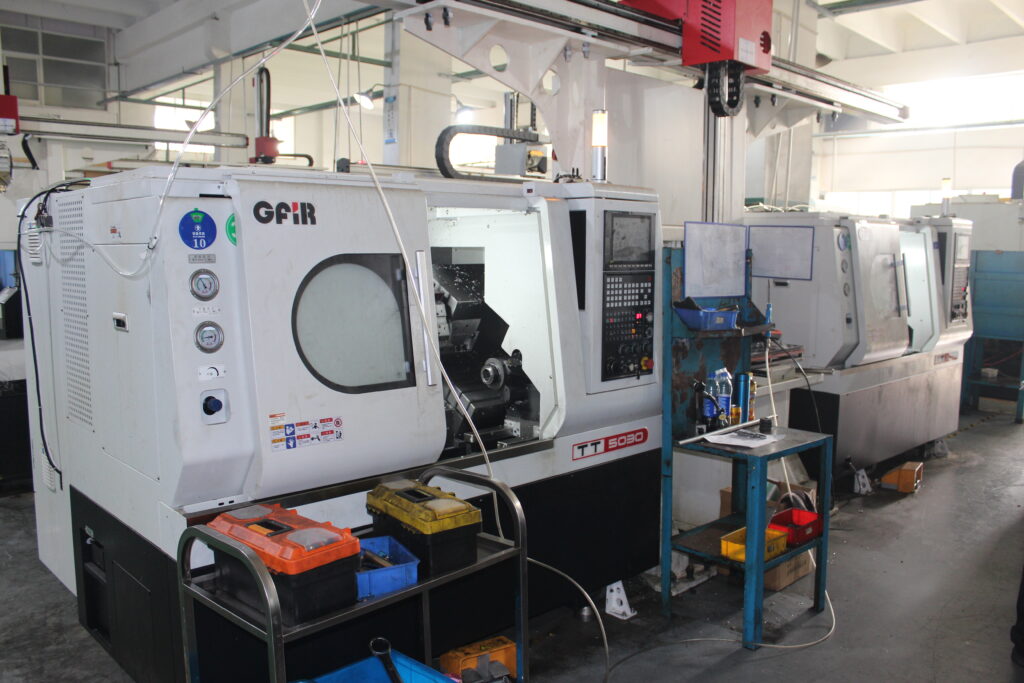




Machines for Swiss CNC Lathe for small parts machining
- Star(+-0.001mm)
- TSUGAMI(+-0.001mm)
- Citizen(+-0.001mm)
CNC 3,4,5 axis for CNC Machining parts
- Gromax(+-0.01mm)
CNC Mill & Turn for turning and milling parts
- DOOSAN(+-0.005)
- Hardanger(+-0.007)
Automatic Lathe with truss for CNC turning parts
- GFIR (+-0.01mm)
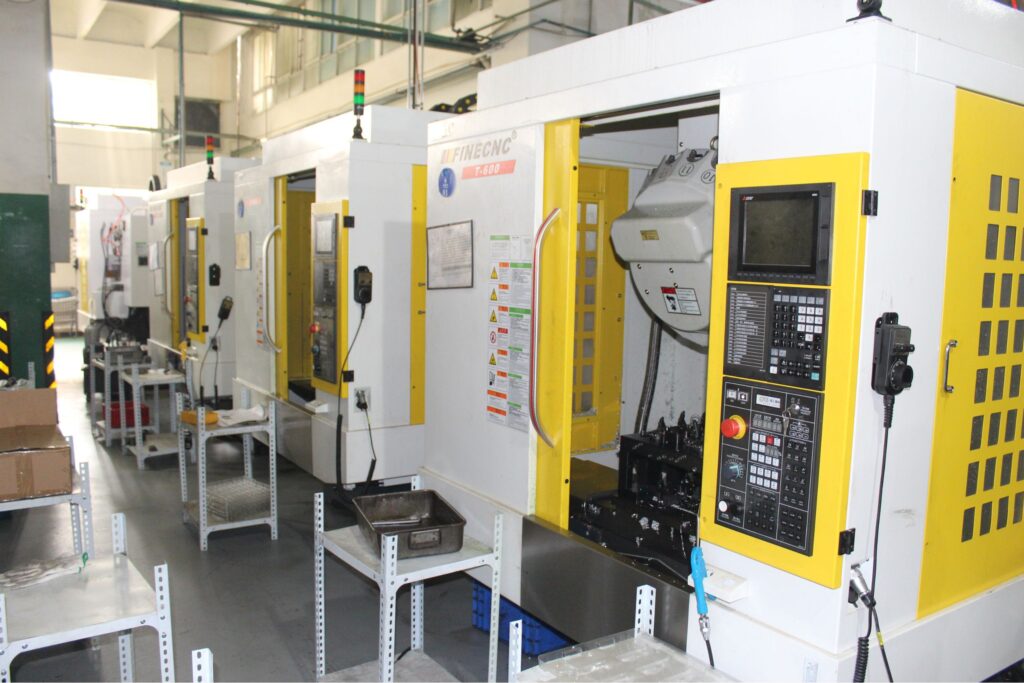
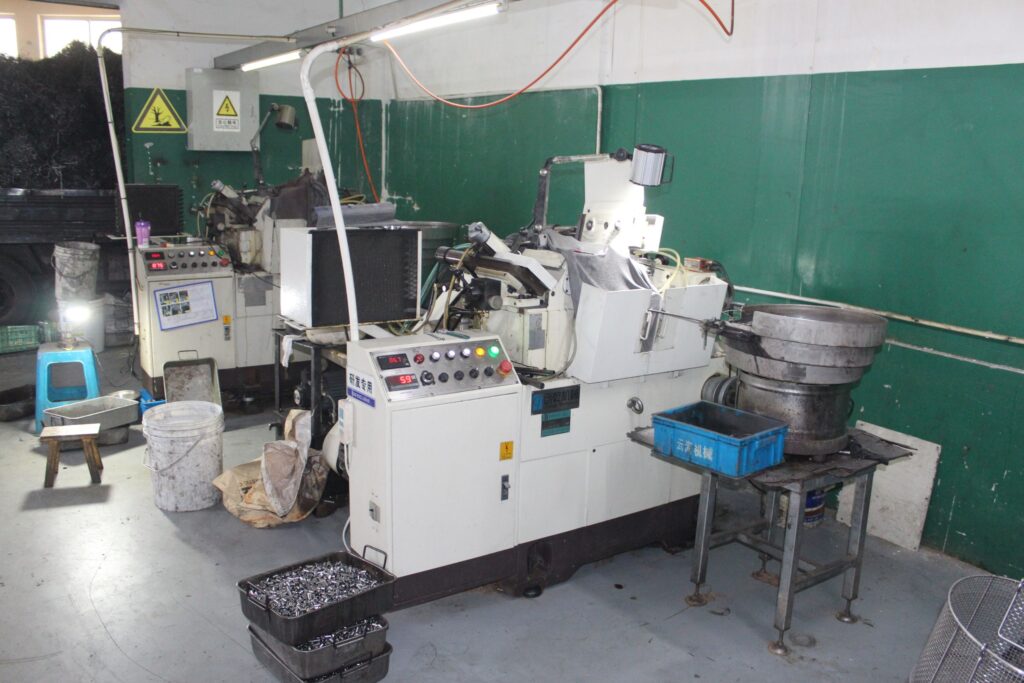




Cam Automatic Lathe for small parts
- MY(+-0.005mm)
Ifine CNC Drilling Machine
Screw Machines for screw
Surface Grinding Machine
- For surface machining
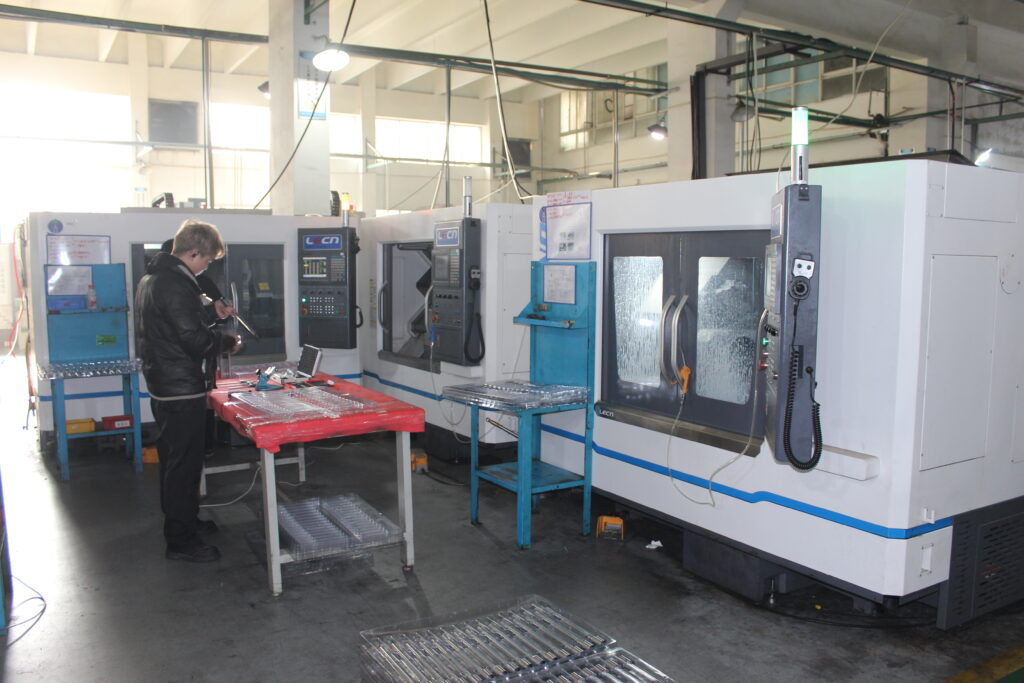
Experienced And Technical Machinist And Inspector
Skilled Machinists with Practical Knowledge:
Quality CNC machining requires qualified and trained machinists. Our machinists undergo a long period of training and accumulating years of practical floor experience. They interpret complicated drawings and read elaborate process sheets without mistakes. Their practical experience is an assurance of easy installation, effective cutting, and adequate usage of the tools. Every machinist is aware of tolerance requirements and machine limitations. This knowledge minimizes mistakes and maximizes output.
Inspectors Protecting Dimensional Accuracy:
Inspectors are essential to quality assurance. They take measurements with precision tools like calipers, gauges and CMMs. They keep track of in-process machining and ensure that parts are up to standard. Inspectors are able to identify deviations fast and impose corrective measures to avoid defects. They check functional fit, as well as cosmetic surface finishes. They avoid rework or rejection at high cost by checking key dimensions twice.
Information Exchange and Data Management:
The junior operators are trained by experienced machinists in order to ensure the quality of production remains consistent. They exchange shared experiences in how to set up, measure, and work safely with machines. The result of this mentoring is good teams and high shop-floor standards. Inspection data is also recorded and saved by the inspectors to be traced in the future. Audits, customer trust and continuous improvement programs are supported by proper documentation.
Closing the Gap between Machines and Quality of Output:
The interface between sophisticated machines and perfect output is made up of experienced machinists and inspectors. Their combined expertise is such that every component is aligned with design intent and industry needs. Through their experience, each part exported is of high quality to customer expectations. Experienced staff is the key to consistent CNC machining excellence.





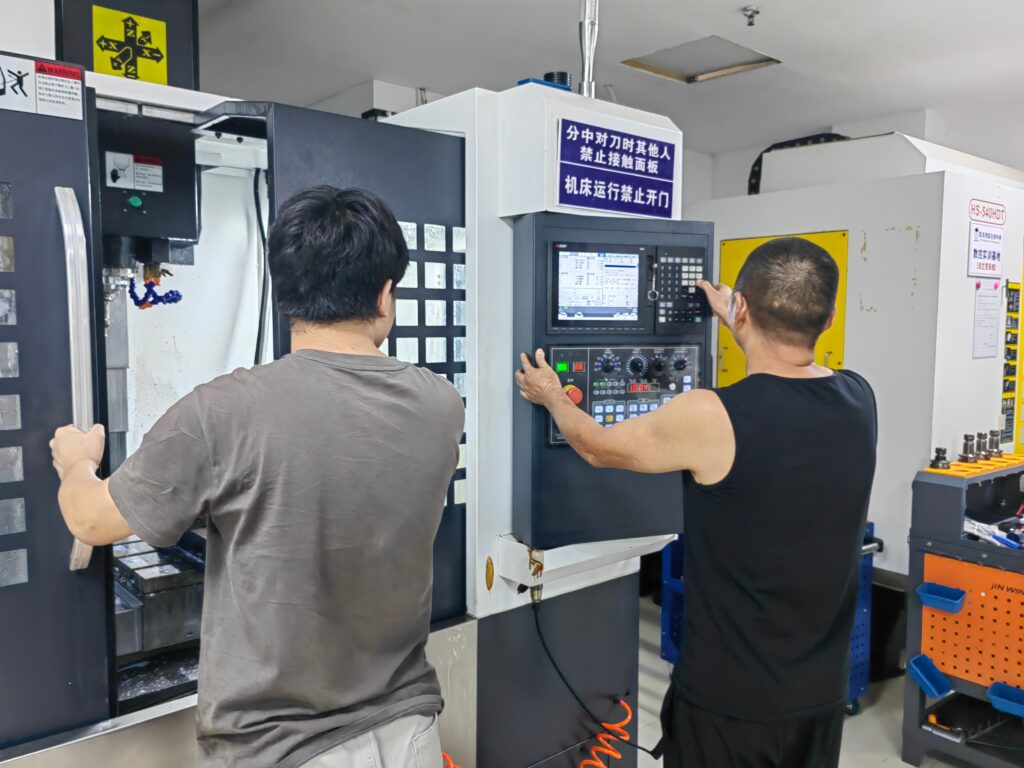
Design of CNC Machining Plan
Production accuracy is based on the design of a CNC machining plan. At CNCSwissMasion, there is accuracy, effectiveness, and flexibility in each plan. CNC requires more planning than traditional machining because it is more automated and more expensive. Having a highly systematized plan minimizes errors and ensures quality in the manufacture of complex parts.
Identifying Part Specifications
The design begins with the definition of part type, size, and model. Before machining, engineers will draw the correct part drawings to make sure that there is no confusion. Functional requirements and dimensional accuracy are captured in each drawing. At CNCSwissMasion, all designs are guided by precision standards. This guarantees parts to be of excellent quality and customer requirements.
CNC Processability Analysis
Then, engineers study the processability of the parts in detail. The hardness of the materials, geometry, and tolerances are monitored. The analysis can be used to detect possible machining problems at an early stage. CNCSwissMasion works with even complicated part geometries with Swiss CNC technology. This level of analysis ensures less expensive mistakes are made in the actual machining.
Establishing Process Route
The machining process route is determined after feasibility checks. Accuracy and efficiency in the sequence of operations are determined by engineers. All operations are meant to lessen waste and enhance the performance of the tools. CNCSwissMasion is a company that values close tolerances and repeatability in all steps of its processes. This guarantees improved production flows and quicker turnover.
Selection of Parameters and Tools
Lastly, parameters and tools are chosen carefully. There is careful optimization of feed rates, spindle speeds and depth cuts. Material compatibility and durability are the criteria used when selecting high-performance tools. At CNCSwissMasion, high precision and surface finish are ensured by advanced CNC parameters. This is done to guarantee high quality in all machined parts supplied.
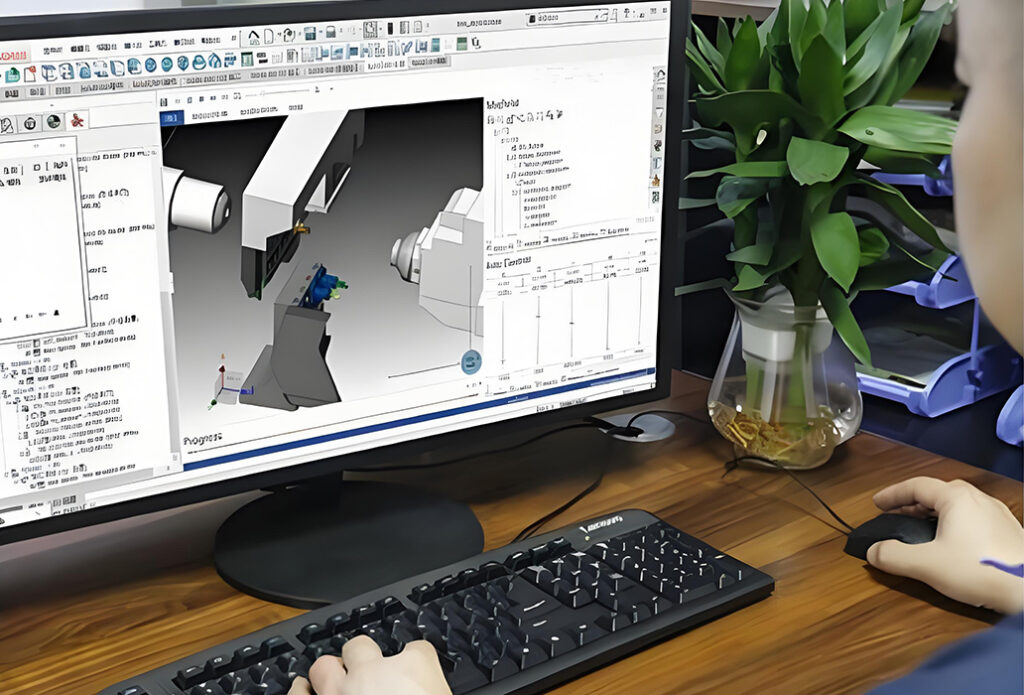
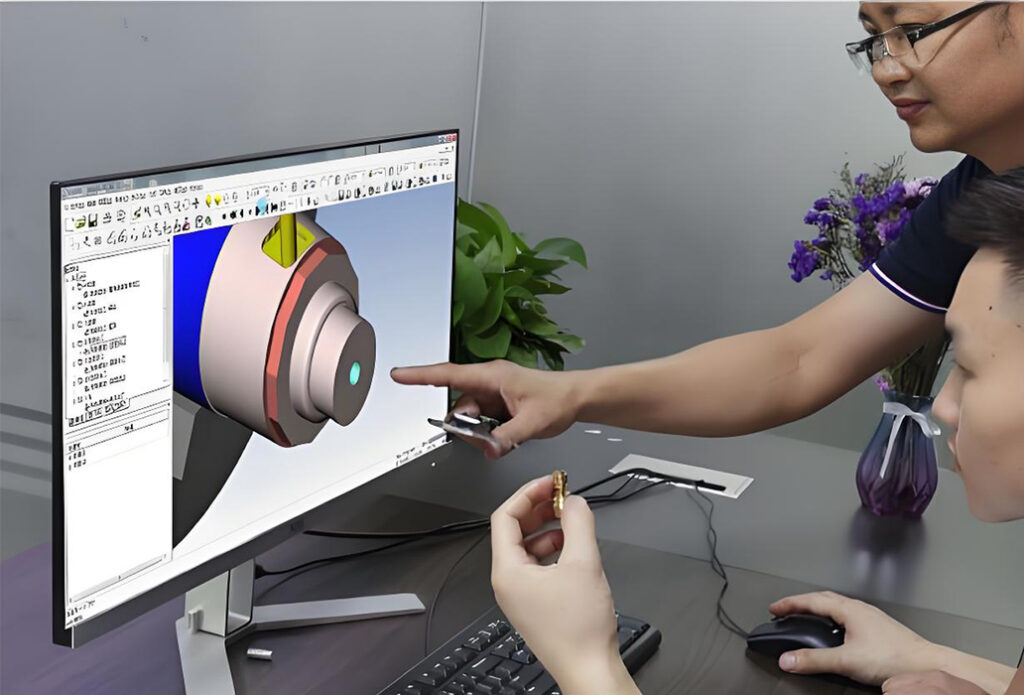

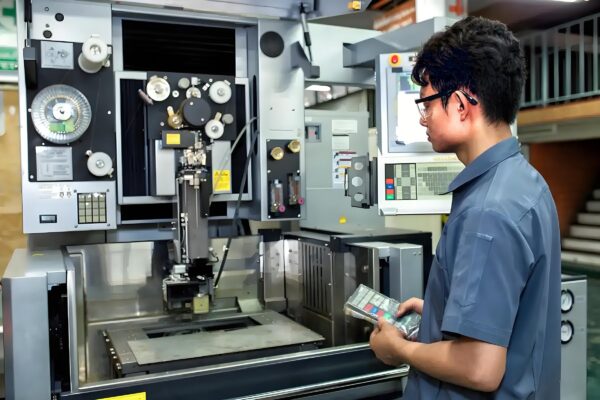
CNC Programming During CNC Machining
In precision machining, CNC programming is an essential factor. Each code of instructions directly influences the end result. Correct models, coordinates and parameters are essential to high accuracy. Swiss CNC machining particularly using CNCSwissMasion is based on the use of perfect programming to achieve unparalleled precision. Quality Parts Parts are programmed correctly to ensure that each part upholds design, quality, and functional requirements.
Significance of Proper Programming: Programming determines the way the machine understands design data. An error-free mathematical model helps to avoid dimensional errors in components. Specifying the coordinate system prevents misalignment in machining. Safety must be provided through tool points and safe planes. Every command has an influence on efficiency and part quality. Even the slightest errors may lead to flaws in components or problems in machines.
Process Planning and Tool Selection: Programming entails organizing every step in the machining plan. Rational sequencing eliminates tool collisions and unnecessary movements. The appropriate selection of tools makes them compatible with materials and tolerances. The tool paths should reduce unnecessary movement and enhance surface finish. The amounts to be cut should be efficient and tool life and accuracy. The programming should be able to adjust to material properties and allowances.
Reduction of Parameters and Syntax Control: CNC programs correspond to machine syntax with instruction letters. Parameters such as feed rate, spindle speed and depth of cut must be accurate. These are based on tool properties and behavior of part materials. Improper parameters may lead to chatter, tool wear or material deformation. These programming decisions are also influenced by the capabilities of the machine tool. Regular syntax is a guarantee of smooth running without any interruption.
Eliminating Mistakes in Implementation: The tool paths should be checked to prevent over cuts or collisions. Checks in programming make sure there is no interference between the tool, the fixture and the workpiece. Clearance planes minimize the risks of crashing. On-Machine Simulation identifies potential machining errors. Close coding avoids delays in production and machine breakdown.


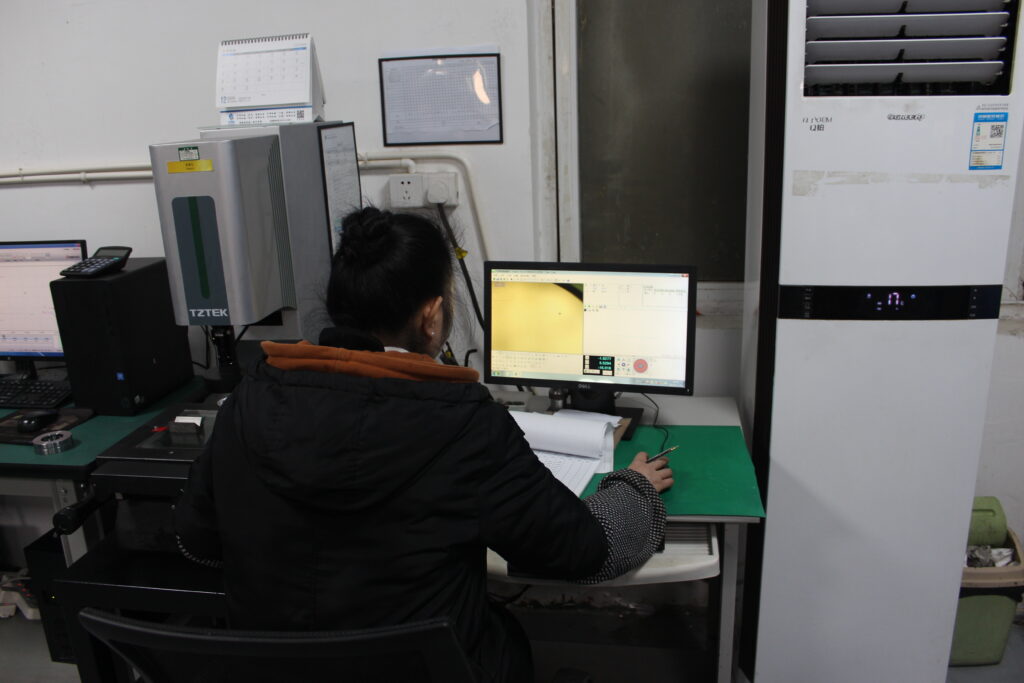
Simulation Inspection Process in CNC Machining
A simulation inspection is an essential process in contemporary CNC machining processes. It assists in detecting troubles prior to the actual machining, which saves time and resources. Manufacturers can guarantee quality, safety and accuracy by integrating physical simulation with geometric simulation. To achieve high precision Swiss CNC machining, CNCSwissMasion uses these processes as a foundation to quality assurance.
Quality Control Physical Simulation:
Physical simulation studies the forces, heat, and vibration of machining. Engineers examine tool stress, spindle load and material response. This process aids in the forecasting of tool wear and possible machine overloads. It also makes sure that machining is stable in actual production conditions. Early detection minimizes the chances of failure of the tools or damage of parts.
Accuracy Geometric Simulation:
Geometric simulation is concerned with machine motions and tool path verification. It is a computer-generated simulation of the whole cutting process in 3D visualization. The engineers verify collisions, interference, and excessive tool engagement. This provides proper tool positioning and axis coordination. It also aids in verifying that design tolerances are in line with actual movements.
Advantages of Simulation Inspection:
Simulation inspection prevents expensive rework and unplanned machine failure. It ensures accurate movement of tools and reduced risks of cutting. It enhances the surface finish and part consistency by avoiding interference. It also increases productivity by minimizing trial runs and wastage. Manufacturers can be assured of a successful run of the machining program.
Position in Swiss CNC Machining High-Precision:
Swiss CNC machining needs high precision with intricate and minute parts. Tight tolerances are always obtained through simulation inspection. CNCSwissMasion relies on these techniques so as to produce quality parts that are free of defects. They ensure high quality machining by using physical and geometric checks.
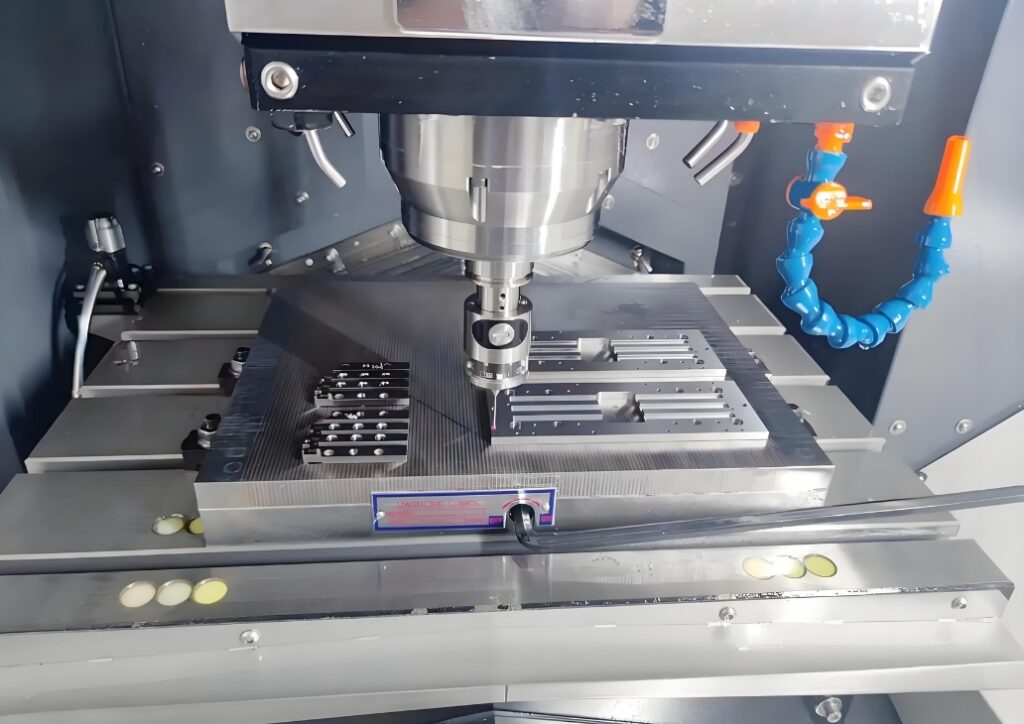
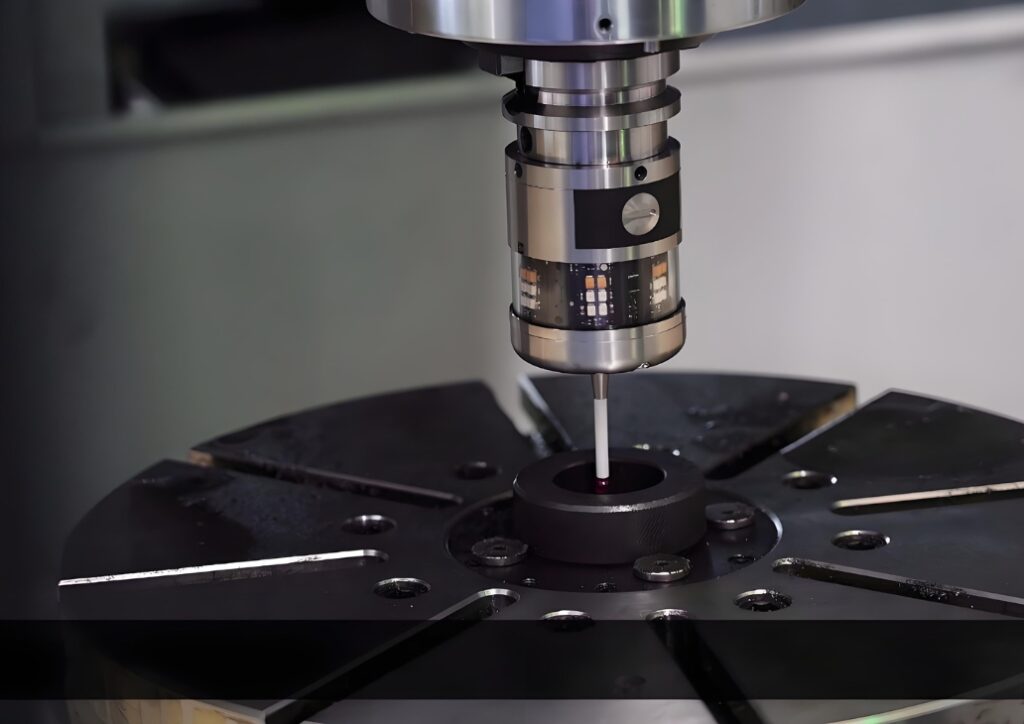


Methods and Tools for Quality Control in CNC Machining
CNC machining requires quality control. Any precision cut depends on systematic checks, planning and feedback. In its absence, defects get higher and efficiency is poor. The CNCSwissMasion CNC machining services rely on high precision quality control systems. Good tactics and equipment ensure uniformity, dependability, and consumer satisfaction.
Process Planning and Control Points: Quality starts with a designed planning. CNC machining steps need to have clear control points. Quality indexes of tolerance, surface finish, and accuracy are defined by engineers. These values are used to conduct inspections in production. The real capabilities of processes should be measured prior to the commencement of machining. Through performance analysis, teams determine weak areas that require control. This planning assures quality checks to fit the project requirements.
Real-Time Analysis and Data Monitoring: Process stability is supported by dynamic monitoring tools. Sensors capture machine information in real time. Vibration and temperature, as well as dimensional accuracy, are monitored. Data obtained is measured against quality indexes. Deviations are analyzed early before they can result in defects in products. Performance trends are depicted in control charts and tables. Real-time analysis allows prompt interventions in case of a change in critical factors.
Statistical and Analytical Techniques: CNC machining is precise with the help of statistical tools. Statistical Process Control (SPC) is frequently used by engineers. SPC monitors changes and ensures that they are within tolerance. Capability studies determine whether the processes are performing as per the design. Root cause analysis is a process that detects the drivers of repetitive defects. These approaches allow corrective actions that reinforce long-term consistency. Systematic assessment ensures that there is constant enhancement over production cycles.
Inspection and Verification Tools: Quality is ensured at various levels through inspection tools. Complex geometries are checked by Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs). Contactless surface profiles are measured using optical systems. Dimensional tolerances are checked in a short time by gauges and calipers. Non-destructive testing reveals faults in some vital parts. Microscopes are measured using digital microscopes in hard parts. Components are machined to the highest standard in each tool.
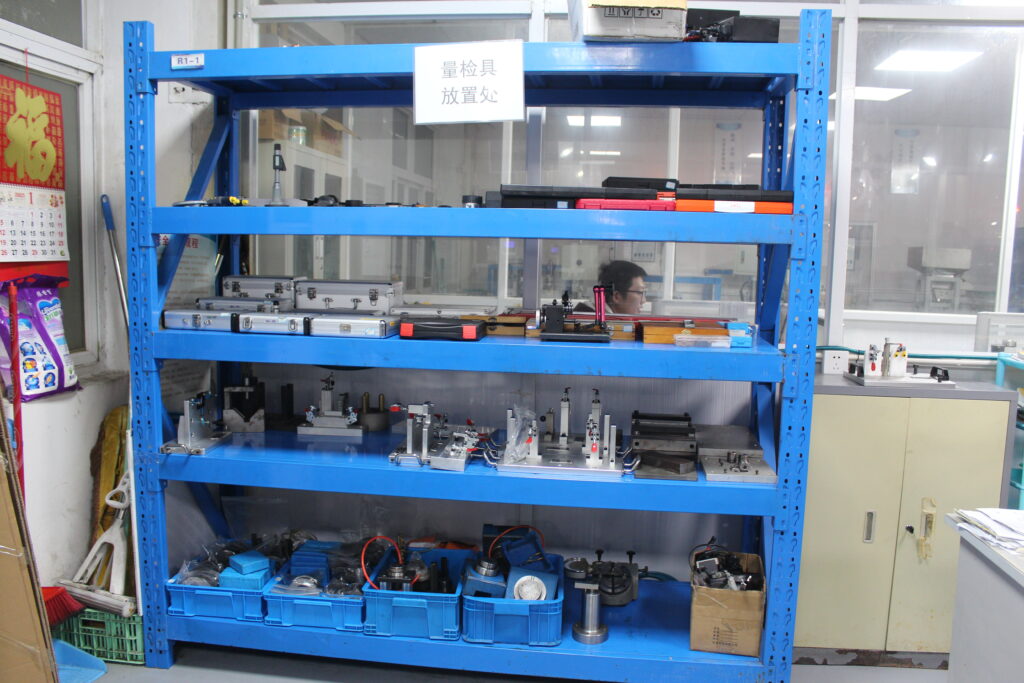


Quality Control Standards
Masion is the leader in precision CNC manufacturing with 21 years of experience. All projects have stringent quality systems. We are certified, which demonstrates our credibility and experience. We are dedicated to surpassing industry expectations and do so with accuracy and consistency.
- ISO9001 Quality Management System.
- ISO14001 Environment Management System Certification.
- TS16949 Automotive Industry Quality Management System.

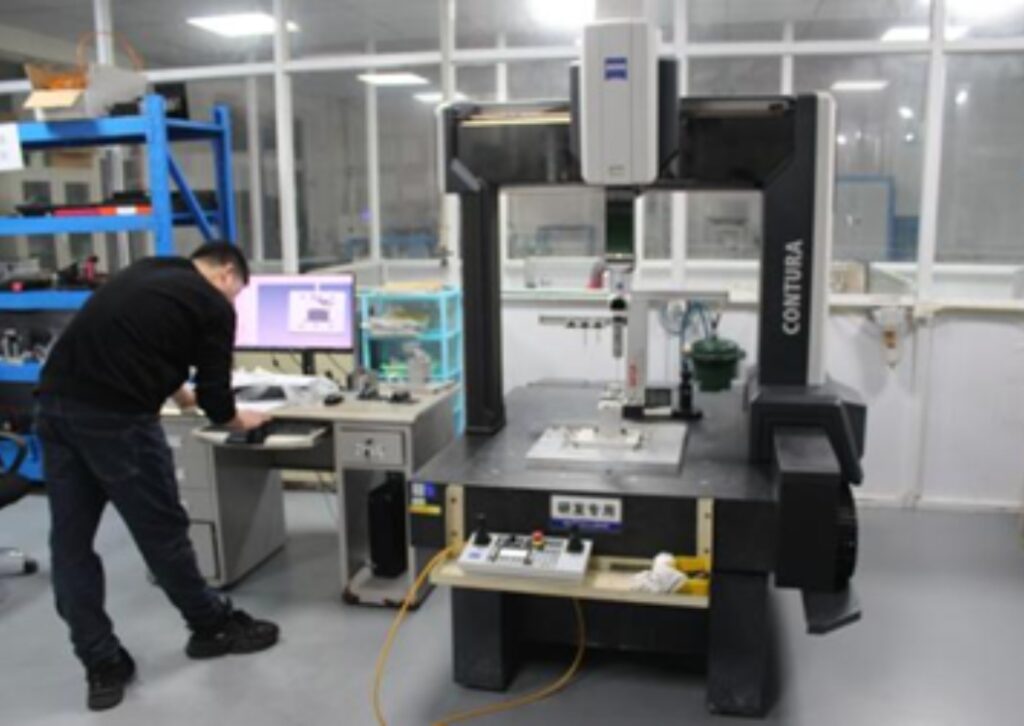
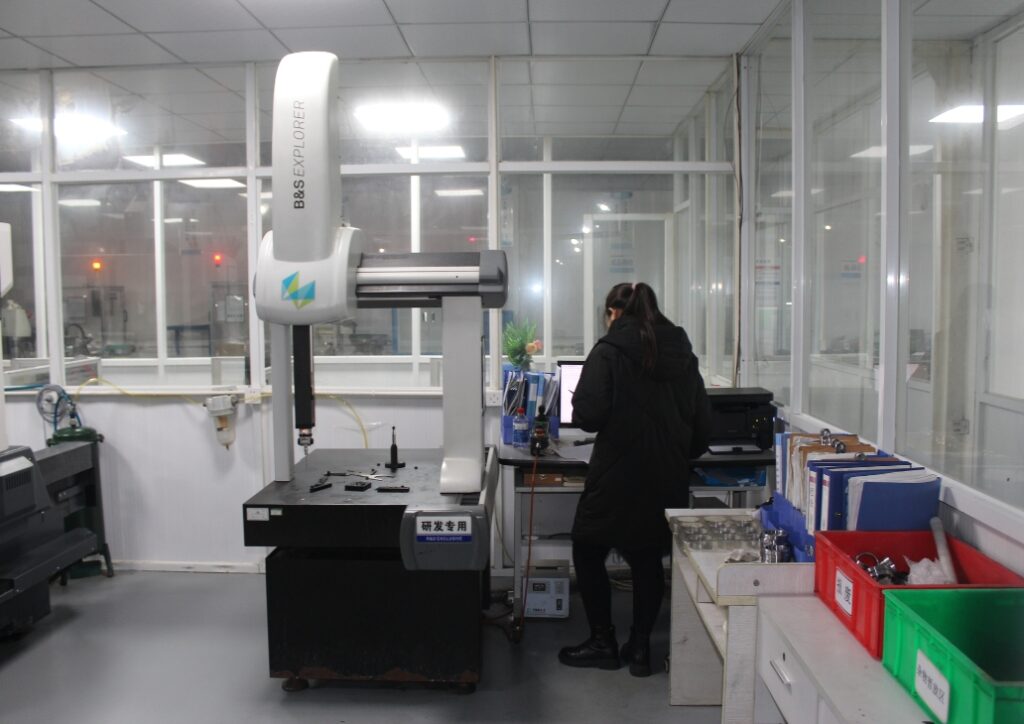
Inspection Machine
Precision in all steps of CNC machining is guaranteed by inspection machines. They verify accuracy, consistency and compliance prior to components being sent to final assembly. In high-level Swiss CNC machining, a minute mistake is enough to affect the performance. These deviations are identified by inspection machines at an early stage securing quality and reliability.
Such systems can measure dimensions, geometries, and surface finishes with a very high degree of accuracy. Coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) prevail because of flexibility and repeatability. Complex geometries can be checked using optical inspection systems. Laser scanning offers fast, accurate digital images to compare with CAD designs. All these technologies combined provide dependable verification of various types of parts.
The inspection machines also make the processes flow smoother since they save time and minimize the number of manual checks. Automated systems also provide consistent results, which reduces operator effects on measurements. This automation assists in keeping a high level of quality control, and this is particularly true in sectors that demand high tolerances. Such consistency is required by aerospace, medical, and automotive manufacturers in order to achieve safe, long-term performance.
Swiss CNC machining services such as that of CNCSwissMasion incorporate inspection as part of it. They achieve high quality in all parts by integrating modern inspection with high-precision machining. These machines are a crucial linkage between manufacturing and validation, which leads to trust and reliability.
Inspection Process
The power of precision CNC machining services is determined by quality assurance. All products should be subjected to stringent checks prior to delivery. These verifications stop flaws, enhance precision and guard customer confidence. At CNCSwissMasion, quality is managed at the materials level up to the shipment.
1) Incoming Inspection
Supplier certificates and reports are provided with all the purchased raw materials. Nevertheless, there are risks when there are mistakes or flaws in materials. We practice rigorous incoming inspection using highly advanced testing equipment. Drawing requirements are compared with material hardness, composition, and strength. Poor materials lead to delays, loss of costs and failures in production. The first stage to prevent this risk is at the incoming stage. Each batch is recorded, tested and approved prior to the onset of machining.
Key checks include:
- Review and confirmation of material report.
- Spectrometer analysis for chemical composition.
- Hardness tests with design tolerance.
- Dimensional checking of bars, rods or plates.
2) In-Process Inspection
Process inspections guarantee precision at each machining process. Prior to clamping, machinists check the workpieces to ensure drawing conformity. The programming guides are compared with workpiece placement. Self-checking occurs after rough machining to identify size errors to correct. Inter-feature positional accuracy is also established. Precision machining does not begin until rough processing has been inspected.
Calipers, micrometers, and gauges are used by the inspectors to check dimensions. Machinists recheck vertical, inclined and shaped surfaces following machining. All semi-finished products are thoroughly checked in terms of size. These measures eliminate flaws and minimize the chances of rework.
Key checks include:
- Tightness and alignment of workpieces.
- Reference edge and positional size compliance.
- Size checking after rough machining.
- Check machining to draw accuracy.
3) Surface Finish Inspection
Product quality is directly related to surface quality and product functionality. Burrs and sharp edges are eliminated after machining. The visual inspection proves smoothness on all surfaces. Goods are tested on their roughness or scratches.
Measurement of surface roughness is done using precision instruments such as profilometers. Stricter checks are required on treated parts, including anodized or painted parts. Finishes on the surface are tested within established limits on the depth of coating and consistency.
Common checks include:
- Measurement of surface roughness.
- Burr and defect confirmation.
- Visual examination in controlled light.
- Coating thickness tolerance.
4) Other Inspection Tests
In addition to dimensional checks, special tests confirm mechanical properties and durability. Salt spray tests are used to test the resistance to corrosion of coated surfaces. Load-bearing strength of critical parts is verified by tensile tests. Hardness tests are used to measure the resistance of the material against deformation and wear.
Impact tests measure the toughness of sudden loads. Long-term reliability of functional components is verified by fatigue tests. Such tests assure that the finished product will work as intended in service.
Included tests:
- Salt Spray Test as a corrosion protection.
- Tensile Test of elongation and strength.
- Hardness Test of wear resistance.
- Impact Test for sudden force absorption.
- Long-term endurance fatigue Test.
5) Pre-Shipment Inspection
Last check-up before making a package. To ensure smooth look, burrs are removed. Dimensional accuracy is checked using CMM, projectors, height gauges, and micrometers. Strict tolerances are re-measured following anodizing, painting or plating.
Tolerance of anodized parts is 0.01mm. In case of powder coating, the tolerance is 0.05mm. Out of this range, products are corrected or rejected. Before shipping, packaging, logos and labels are independently checked. This keeps the customer with products that are correct, free of defects and of professional quality.
Key steps:
- Burr removal and visual surface inspection.
- Complete dimensional measurement.
- Re-check of surface treated parts.
- Checking of labels and package compliance.
Explore our Range of Products
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of CNC quality control in the case of everyday products?
CNC quality control means that products are fit, operate and have longer lifespan. It is essential to it as it can break down the numerous components in a car as well as in medical equipment.
What is the impact of CNC quality control on the safety of products?
It eliminates flaws that may lead to accidents or failure. CNC control checks the strength, dimensions, and surface quality to make sure that parts remain trustworthy in their application.
Are there quality standards that are adhered to by all CNC manufacturers?
Not always. Others may not be subject to strict ISO or automotive standards. Selecting certified factories minimizes risk and ensures uniformity.
What are the tools of CNC quality checks?
Calipers, gauges, CMMs, and microscopes are used by inspectors. These are size, surface finish and hidden flaw measuring tools to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Will CNC quality control reduce the cost of manufacturing?
Yes. It prevents rework, waste, and recalls of the product by detecting defects at an early stage. Good quality systems enhance efficiency and cost less in the long term production.
What are the benefits of strict CNC quality control to the customers?
They obtain high quality, reliable, and safe goods. The quality control also assures specifications in deliveries, which creates customer trust and decreases complaints.
Do small CNC parts also require quality control?
Absolutely. Even minor elements, such as screws or connectors, influence performance. A low quality of miniature components can cause serious failures.