Types of Shafts – Materials, Perks, Problems, and More
You cannot deny the importance of the right shaft. There are a variety of shafts exists, each featuring different materials, construction, and purpose. Knowledge on the key facts of shafts is crucial to make the right selection. Wrong selection can lead you to face wear and tear, inefficient functioning, expenditures, replacements and more. No need to worry this guide will serve the purpose. You will find insights on the key shaft types, materials, their functionality, applications, and more. By reading this guide you will be able to make the right choice. Sounds captivating? Let’s dive right in to uncover the facts!
What is Shaft? – Defining Shaft
Table of Contents
ToggleYou can define shaft as a rotating component which is responsible to transfer power in machines. With the shaft you can connect various components including gears, pulleys, and other mechanical parts. The shafts are present in engines, motors, conveyors, etc. Selection of right shaft will lead you to experience effective energy transfer. Knowing the role of the shaft will help you tweaking machine longevity and performance.
Key Materials Used in different Types of Shafts
| Sr. No. | Shaft Type | Common Materials | Key Properties |
| 1 | Solid Shafts | – Carbon Steel (AISI 1018, 1045) – Alloy Steel (AISI 4140, 4340) – Stainless Steel | – High strength – Good fatigue resistance – Relatively low cost |
| 2 | Hollow Shafts | – Carbon Steel – Alloy Steel – Stainless Steel – Aluminum Alloys | – High strength-to-weight ratio – Reduced weight compared to solid shafts – Used where weight is critical |
| 3 | Composite Shafts | – Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) – Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) | – Very high strength-to-weight ratio – Excellent fatigue resistance – Used in applications requiring lightweight and high performance |
| 4 | Ceramic Shafts | – Silicon Nitride – Zirconia | – Extremely high hardness and wear resistance – Excellent corrosion resistance – Used in high-temperature and high-wear applications |
Types of Shafts – Revealing Every Single Type
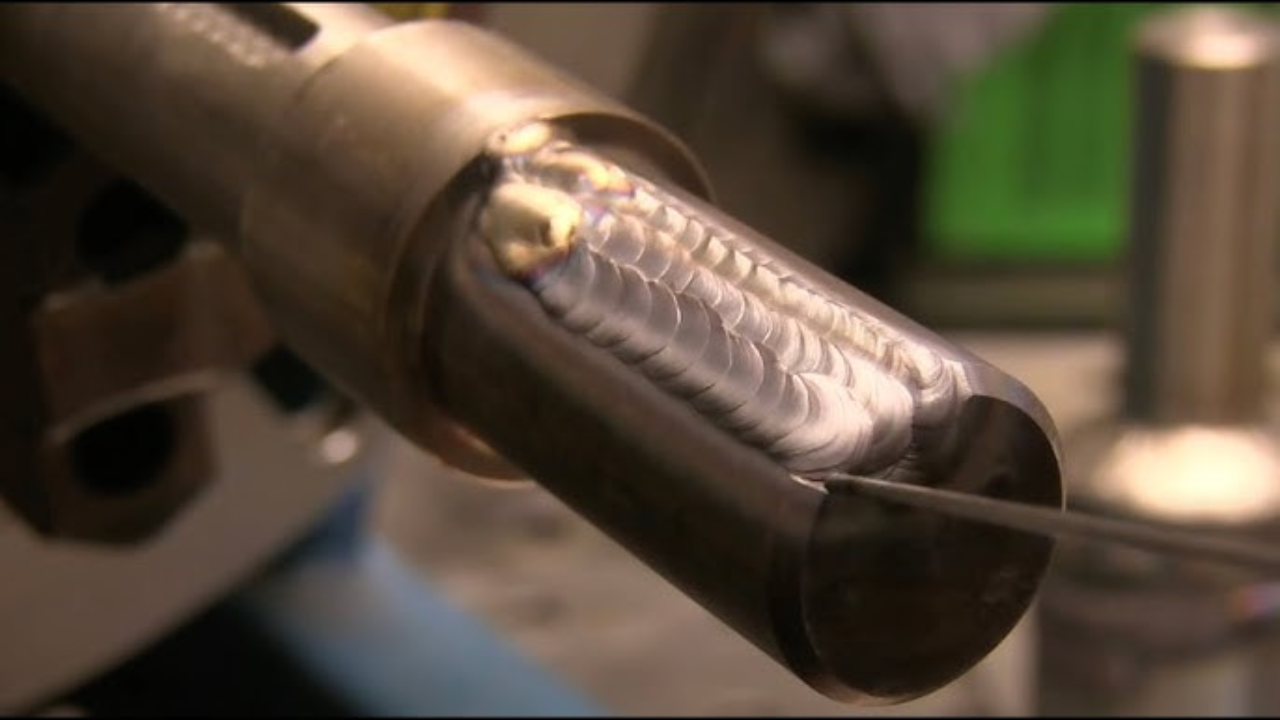
Welded Shaft
The concept of a welded shaft is that smaller parts are welded together, creating one continuous piece. The shaft provides for power transmission and is widely used in various industries. Steel and high strength alloys are often used because they are welding compatible and durable. Welded shafts come in customizable lengths and have enhanced strength making them perfect for heavy duty applications. However, poor welding can cause joint failure. Issues like this can be prevented through regular inspections and proper welding techniques.

Wiper Shaft
A wiper shaft powers the wiper mechanisms of vehicles. This makes it easy to move the motor to the wiper arms and clean windshields properly. The wiper shafts are usually constructed of corrosion resistant material such as stainless steel, to resist continuous wetting with moisture. It makes for smooth, consistent motion for good wiper performance. Rust, wear from usage and misalignment are a few of the issues. If lubricated regularly and parts are replaced as needed, it can run.

Motor Shaft
The motor shaft is a central rotating part of electric motors. It transmits torque from the motor to other parts of the system. Industrial equipment, home appliances and vehicles all rely on these shafts. Hardened or stainless steel that is treated for wear and heat. Motor shafts provide efficient torque transmission with minimal energy loss. Some common problems are: vibration, misalignment, bearing wear. Regular maintenance and proper adjustment of the alignment can avoid these issues.

Gear Shaft
Gears are connected to a gear shaft and rotated in mechanical systems in order to transmit power between them. Gear shafts are found in automotive gearboxes, machinery and industrial equipment. High strength steel and alloy materials that can withstand stress and torque are preferred. Their performance and durability are good. It can lead to gear teeth wear, misalignment and lubrication failure. Premature wear and reduced efficiency of the system can be prevented through proper maintenance and proper lubrication.

Industrial Fan Shaft
Industrial fan shaft is used to link the motor to the fan blade for neat air flow in ventilation systems. These shafts are common applications to the HVAC systems, industrial fans, and other air circulation equipment. Corrosion resistant steel and alloys resist the environmental factors. A stable rotation industrial fan shaft guarantees the correct ventilation and air flow. Common causes are vibration, imbalance and bearing wear. This can extend the time period of proper installation, balancing and routine maintenance and service life of the system, therefore reducing the incidence of system problems.

Air Condition Shaft
The key components of air conditioning systems such as compressors or fans are powered by an air condition shaft. Commercial and industrial HVAC units also use it. Made from high quality steel or aluminum to resist wear and temperature fluctuations. Reliable airflow and cooling efficiency is dependent on the air condition shafts. Performance is affected by bearing failure, overheating, or corrosion. Regular cleaning, lubrication and inspection ensure that they do their job well without a malfunction.

Square Bore Shaft
For the square standard bore, square shaft bore shaft has a square square cross section and fits into the same square bore. However, it provides secure coupling and efficient torque transmission, making it an appropriate solution for automotive, agriculture and machinery applications. They are made of high stressed materials such as steel or stainless steel or alloys which can tolerate the stresses and bend to shape. No slippage and reliable performance for square bore shafts. However, it is possible for these parts to wear or go out of alignment, even if they are part of a regular inspection, if they are not checked regularly or at all.

Axle Shaft
They are also important as they transmit engine to wheel power in vehicles and industrial equipment. The IC is ruggedized for use in severe conditions under high torque and heavy load. Steel and alloy materials with surface treatments can provide such strength and durability. Vehicles and material handling equipment often include axle shafts. However, they may get damaged or skew sometimes, however, they can be fixed by timely repairs and maintenances.

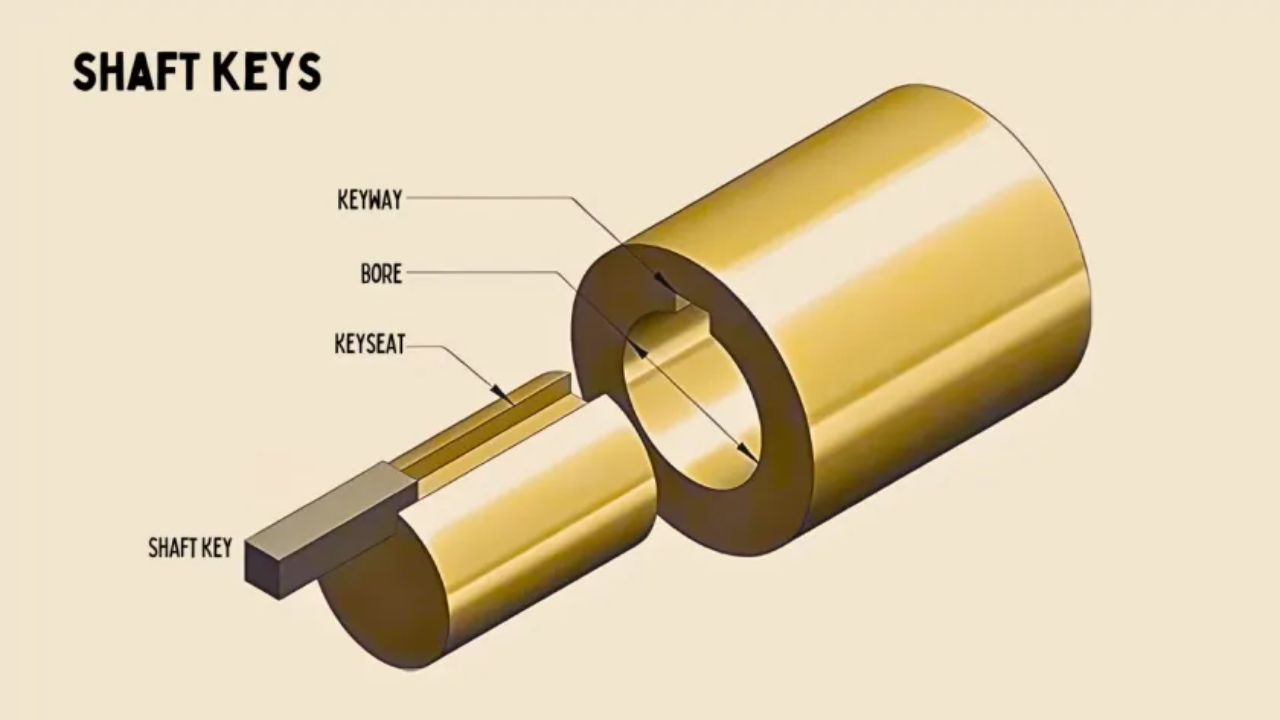
Keyed Shafts
Slotted Shafts: These shafts have slots cut into them into which keys can be placed to prevent the slippage of connected components. Used in motors, rotary equipment, and gear systems. For other applications like flat and square. Keyed shafts provide a strong and secure connection between parts and provide strong and reliable power transmission. However, there can be problems like keyway wear, misalignment or shaft damage, but if the design and maintenance are considered these are avoidable.
Machine Shafts
This is a part which can be used in making machines to transmit the rotation of the machines, or a machine shaft. Motors, conveyors and other gear systems also use it. Usually, shafts are made of stainless steel, carbon steel or hardened alloys for strength and durability. The theory is then applied to various fields. Bending, wear, corrosion and misalignment are some of the problems that they have. Each time the materials are properly selected and regularly inspected to ensure you get the best performance and longevity.

Drive Shaft
The drive shaft is actually transferring the mechanical power from an engine to parts like wheels or gears — but this is not something that traditional parts would do. It is also effective and compulsory for high torque systems for better power transmission. It is well known that drive shafts are used in automobiles, aircraft and agricultural machinery. Stress materials that can be used over a long period of time. Some common problems include vibration, wear and lubrication. For example, greasing, inspection for wear, etc will prevent failure and extend its life.

Flexible Shaft
It is flexible shaft, which means that it is able to transmit power in relation of bends and curves, which is ideal for situations with limited space. These shafts can be found in tools, machinery, and motor vehicles. They are made of steel or aluminum with flexibilities. They can reach hard to reach places and get a rotation of the power in regular way. However, they can tire out and be worn out. To run long and hard, they must be properly lubricated and regularly maintained.

Spindle
Spindle holds tools, work pieces and performs rotational tasks. Usually found in lathes, milling machines, and other CNC equipment. Precision alloys or hardened steel is used for spindles, fitting with bearing configurations for smooth running. They are able to give high precision rotation at high speed. This can lead to bearing wear and thermal expansion. It also checks for alignment, and replaces the bearings on a regular basis.
Transmission Shafts
Within the car’s transmission system, these transmission shafts are used to move power from one part to another. They’re needed for automotive, heavy machinery, and industrial machines. They are made of high strength steel capable of taking in torque and sustaining stress. These shafts reduce friction, provide smooth power transfer, and improve performance. Common problems include misalignment, overheating, and wear. Regular inspections and proper lubrication can also prevent these alignment problems and reduce wear.

Countershaft
In gear systems, a countershaft is used as a secondary shaft to transmit power. They are used in gearboxes, automotive transmissions and industrial gearing. The countershafts comprises of steel alloy material that can bear high speeds and stress. Hence they can improve efficiency and enable multi-speed transmission. This can lead to problems like gear wear, misalignment, overheating, etc. Regular gear inspections and cooling system checks are carried out.

Graphite Shafts
Lightweight and strong, graphite shafts are made of composite materials. Sports equipment, such as golf clubs and fishing rods, as well as aerospace applications, rely on them. Their corrosion resistance and vibration damping properties make these shafts excel in high speed tasks. But they are prone to brittle fractures and impact damage. They are maintained by careful handling and routine checks for cracks.

Spline Shaft
Spline shafts have grooves which mate with another part’s corresponding grooves to transmit torque. These shafts will be used to power automotive parts, industrial machines, power tools and other similar areas. Spline shafts are made from steel or stainless steel, and they minimize slippage to transfer power efficiently. Wear, misalignment and lubrication are problems. To keep them in good working condition, they require regular lubrication and proper alignment checks.

Cardan Shaft
A cardan shaft connects the rotating parts of machines and drive systems with flexibility. Therefore, these shafts are extensively employed in automotive and industrial applications. As they are made of high strength steel, they can be used under stress. Power transmission and movement between connected components is allowed by the cardan shaft. These include fatigue, misalignment, and ultimate joint damage. By inspecting joints regularly and realigning them, costly repairs can be prevented.

Eccentric Valve Shaft
The eccentric valve shaft rotates off center to create uneven motion for specific functions. These shafts are used to power camshaft engines, centrifugal machines and vibrating equipment. Alloy steels are used in their construction and can stand up to high stress applications. Eccentric shafts may also undergo wear, misalignment and vibration issues, and produce specialized motion. Smooth operation requires proper alignment and vibration monitoring.

Hollow Shafts
Hollow shafts feature a hollow core that reduces weight while maintaining strength. High speed machinery, aerospace and automotive sectors often use them. The shafts are made of high strength steel, aluminum or composites for superior strength to weight ratio. They are lightweight and offer better torque transfer. But they can become fatigued and crack due to impact. Long term performance is ensured with regular inspections and cautious handling.

Idler Shaft
Idler shaft is used for transmitting power without bearing the load through idler gears. It is used in gearboxes, mechanical systems and automotive applications. Strong alloys are required for durability and smooth operation. It is optimal for transferring motion and torque, but not carrying a load. However, misalignment and wear in the gear is also common and it needs to be maintained and checked properly for alignment to avoid unplanned downtime.

Main Shaft
Main shaft is the backbone of any system that carries most of the load. This is commonly used for strength in turbines, engines and heavy machinery. High strength alloys are required for maximum performance under demanding conditions. It can carry heavy loads and transfer motion efficiently. Nevertheless, problems such as wear, bending or fatigue can arise, yet regular inspections and timely replacement will ensure your system continues to run smoothly.

Propeller Shaft
It is a propeller shaft which propels a propeller and is used for marine and aerospace propulsion. That’s common on ships, submarines, and aircraft. Corrosion resistant materials like stainless steel, offer reliability in harsh environments. Without this shaft, a key component of these systems, propulsion wouldn’t be possible. As corrosion, wear, and misalignment are common problems, proper material selection and routine maintenance can reduce or eliminate them.

Pump Shaft
A pump shaft receives the power from the motor and transfers it to the pump. It is applied in water pumps, industrial machines and chemical manufacturing plants. As they are corrosion resistant, they are made of stainless steel, carbon steel, or composite materials. Pumps run smoothly and efficiently. Regular checks are also required to wear, corrosion and maintenance needs, which are necessary to prevent such costly repairs.

Shaft Manufacturing Processes
Forging
In its simplest form, forging is the shaping of metal through compressive force at high temperatures. It increases the strength, durability and uniformity of the shaft. Forged shafts are widely employed used in auto, energy and heavy machinery sectors.
Machining
In this process the stock material is cut down from raw material using mills or lathes. The process can be very precise and tailored to suit shafts. This is commonly employed in automotive and aerospace industries to meet exact specifications.
Casting
Shafts are formed through casting, in which molten metal is poured into molds. For mass production or high complexity geometries, it is economical and better. Although casting has a very non uniform strength thus making it an unfavorable form for the high stress applications.
Heat Treatment
The shafts are also strengthened through heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering which change their microstructure. Increasing hardness, toughness and fatigue resistance to enhance durability in demanding situations. Heat treatment is crucial in the industries where high performance shafts are to be fabricated.
Shaft Applications
Power and mechanical performance are obtained by transmitting power by shafts in many fields. Here’s how they are used across sectors:
Automotive Shafts
Different shafts are found in cars like the drive shaft, axle shaft, camshaft etc. The transmission of engine power to the wheels is vital, and the vehicle’s performance and efficiency is improved.
Industrial Machinery Shafts
Shafts ensure smooth operations in manufacturing or processing equipment. Such systems are conveyor shafts, gearbox shafts and pump shafts in industrial systems which are highly reliable.
Aerospace Shafts
To safely operate an aircraft, specialized shafts like engine and control system shafts are required. These are designed to meet rigorous performance requirements using lightweight, high strength materials.
Marine Shafts
Propeller and rudder shafts are essential to the navigation of boats and ships. These shafts are made of corrosion resistant materials so that they can resist saltwater environment.
Shaft Selection Criteria
Load Capacity:
Load requirements are determined before a shaft is chosen. Calculate the force or weight the shaft will be subjected to during operation. Choose materials that have high strength, and design load bearing for the increase in the load capacity. A well designed shaft will not deform and fail under stresses because it does not let the shaft deform and fail.
Rotation Speed:
Consider how fast the shaft will spin. For high speeds, materials are needed that resist fatigue and remain durable. Pick out RPM (revolutions per minute) and find the shaft type for it. Good selection is important for optimal performance and longevity.
Environmental Factors:
Where the shaft is operated, conserve the environment. Corrosive, high temperature or chemically rich conditions require special materials. For reliability, shafts made from stainless steel or heat resistant alloys should be chosen for marine or extreme environments.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations:
When selecting a shaft, make sure to balance cost with performance. High strength materials can increase the cost but improve durability. Look at manufacturing methods that are just your budget, but still efficient. Material, manufacturing and long term cost effectiveness weight trade offs.
Shaft Failure and Maintenance
This amounts to being efficient in terms of understanding shaft failure and acting upon it. You can increase reliability and reducing downtime by finding causes and practicing good maintenance practice.
Common Causes of Shaft Failure:
- Fatigue: The shaft becomes weak and cracks and breaks over time as a result of repeated stress cycles.
- Misalignment: If the shafts are not aligned (misaligned) then all the stresses are not equal and the shafts will wear prematurely and fail.
- Wear and Corrosion: Shaft surfaces are continuously degraded due to exposure to corrosive elements or due to friction.
- Improper Design or Material Selection: When they are using materials that can’t support the load demands or design choices.
Shaft Maintenance:
- Lubrication: Use appropriate lubricants to reduce friction and avoid overheating.
- Alignment Checks: Ensure that shafts are checked and aligned on a regular basis to achieve balanced load distribution.
- Routine Inspections: This will help you check for wear, cracks, or corrosion to catch issues early.
- Extend Lifespan: Select good materials and try to reduce operational stress.
Repair and Replacement:
- Repair Options: Techniques such as welding or re-machining restore minor damage to functionality.
- Replacement Considerations: Only check shafts at regular intervals or when the cost of repair exceeds the benefits or where safety is an issue.
Advanced Shaft Technologies
Magnetic Shafts
Magnetic shafts revolutionize the management of friction and wear in mechanical systems, operating exceptionally well in a wide array of typical conditions and situations. These shafts use magnetic fields to reduce direct contact between components and to eliminate the need for maintenance. They are so efficient that they are ideally suited for the precision equipment and high tech industries such as robotics and medical devices.
Sensors and Monitoring: Sensors and Monitoring (Smart Shafts)
Smart shafts include sensors that provide real time performance data. You can monitor load, speed, and temperature directly. These innovations are revolutionizing industrial machinery, automotive systems and aerospace applications by improving efficiency and eliminating breakdowns. Smart shafts are more controllable and predictive maintenance.
Conclusion
The understanding of the various shaft types is crucial to make the right selection. Shaft exists in the market in variety of materials, types, purpose, and forms. Multiple things including the weight, strength, your need, toughness play a decisive role in selection. Now you have read the above article and have insights on these features and considerations. Select the right shaft today for your needs to harness optimum perfromance, efficacy, and negligible maintenance.
