Inconel 718 – Properties, Applications, and CNC Machining Insights
The Inconel 718 is a vital superalloy that finds extensive application in the aerospace, power generation, and petrochemical sectors owing to its superior strength, corrosion and high temperature capability. You must learn about it thoroughly since its special composition, microstructure and machining characteristics directly influence component life, tool life, and precision results. The purpose of this article is to offer a comprehensive reference on Inconel 718, its history, chemical structure, strengthening effects, CNC machining factors, use, and limitations and best practices in producing durable, high-quality parts.
Table of Contents
ToggleHistory and Development of Inconel 718
Inconel 718 was developed in the 1960s as INCO developed Inconel 625. You are to know that it was originally designed on high-performance steam-line piping. With time, it became a common superalloy in aerospace, petrochemical and power generation sectors. The major research achievements enhanced its mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature strength. Inconel 718 is popular in CNC machining today because it is more reliable and can work in harsh conditions. Its history aids you to understand its uses and machining aspects.
Inconel 718 Chemical Composition and Alloying Elements
Inconel 718 refers to a nickel-based superalloy which is created to be high strength and resistant to corrosion. It has an average chemical composition of Nickel (Ni) as the base element, which gives it structural stability. Chromium (Cr) increases oxidation and corrosion resistance whereas Iron (Fe) stabilizes the alloy matrix. Addition of such strengthening elements as Niobium (Nb), Molybdenum (Mo), Titanium (Ti), and Aluminum (Al) enhances performance and hardness at high temperatures. Major components like Carbon (C), Cobalt (Co), Manganese (Mn) and Silicon (Si) refine the grain structure and enhance the mechanical properties. This knowledge of this composition will assist you in choosing the appropriate grade of CNC machining, cutting parameters, and the life of tools and still preserve dimensional accuracy and surface integrity.
Element | Typical Content (%) | Primary Role / Function | Impact on Properties | Relevance to CNC Machining |
Nickel (Ni) | 50–55 | Base element | Provides structural stability, toughness, and high-temperature strength | Forms the main matrix; understanding content helps predict cutting behavior and tool stress |
Chromium (Cr) | 17–21 | Corrosion and oxidation resistance | Enhances resistance to chemical attack and high-temperature oxidation | Supports surface integrity during machining in oxidizing environments |
Iron (Fe) | 17–21 | Matrix stabilization | Balances alloy composition, maintains ductility | Influences work hardening; affects tool load during cutting |
Niobium (Nb) | 4.75–5.5 | Precipitation strengthening | Forms gamma prime (γ’) phases for high-temperature strength | Increases hardness; requires careful feed and speed selection to reduce tool wear |
Molybdenum (Mo) | 2.8–3.3 | Solid solution and strengthening | Improves creep and high-temperature resistance | Impacts cutting forces; higher Mo increases tool stress |
Titanium (Ti) | 0.65–1.15 | Precipitation strengthening | Contributes to γ’ phase formation, enhancing toughness | Tool wear can increase due to localized hard zones |
Aluminum (Al) | 0.2–0.8 | Strengthening element | Supports γ’ phase, improves high-temperature performance | Affects chip formation; requires optimized cutting parameters |
Carbon (C) | 0.08 max | Grain refinement and carbide formation | Improves wear resistance, prevents grain growth | Hard carbides increase tool wear; careful tool selection needed |
Cobalt (Co) | 1.0 max | Solid solution strengthener | Enhances hot hardness and thermal stability | Reduces thermal softening of tools; still requires cooling management |
Manganese (Mn) | 0.35 max | Deoxidizer and toughness enhancer | Improves ductility and impact resistance | Minimal effect on machining; supports smooth chip flow |
Silicon (Si) | 0.35 max | Deoxidizer and strength enhancer | Maintains oxidation resistance and overall alloy stability | Helps avoid scale formation; limited impact on cutting behavior |
Microstructure and Strengthening Mechanisms
Base Matrix
Inconel has a FCC (face-centered cubic) austenitic structure as its base matrix. This matrix offers high ductility which means that the material is able to deform and does not crack under stress. It is also a major contributor to corrosion resistance to safeguard parts in inhospitable environments. This knowledge of this matrix will make you admire how Inconel is tough and yet resists a chemical attack. It is flexible and stable, which is the basis of all strengthening mechanisms that you can find in high-performance applications.
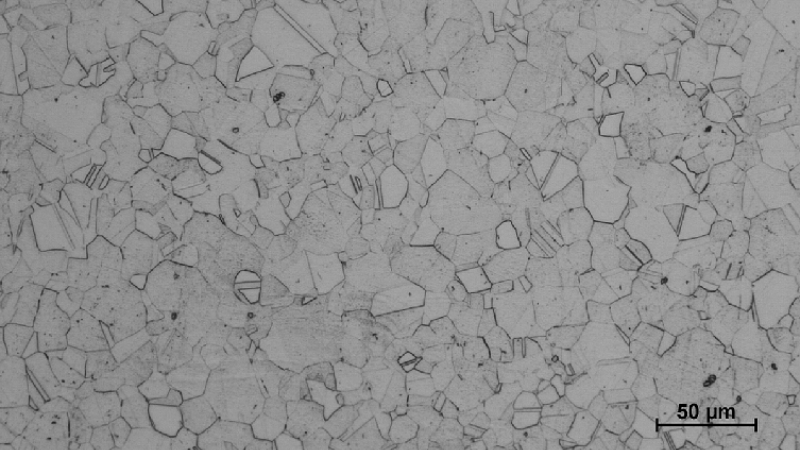

Key Strengthening Phases
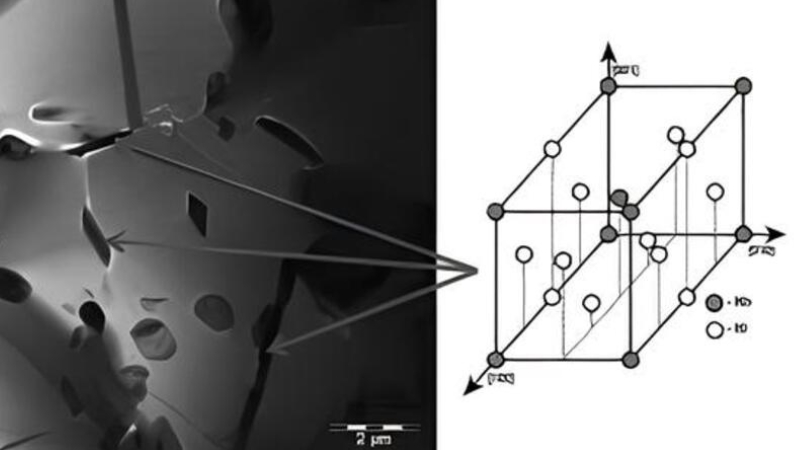
γ’ Phase (Ni₃(Al, Ti, Nb))
The FCC matrix is completely compatible with the γ’ phase, which is thermally stable. It serves as a great obstacle to dislocation motion, enhancing material strength. Anti-phase boundaries are created in γ and this enhances resistance to deformation. As you think of high-temperature uses, γ’ allows structural integrity and creep retardation. It is also important in aerospace and turbine components since it is uniformly distributed throughout the alloy, giving it uniform strengthening.

γ’’ Phase (Ni₃Nb, BCT)
Both γ and γ give the same lattice mismatch, which makes γ’ more strengthening as compared to γ. You have increased creep and fatigue, at higher temperatures. Its existence stabilizes the microstructure during cyclic loads, enhancing alloy life. γ’’ creates very small precipitates that hinder dislocation motion to a greater extent, which improves performance at high temperatures. Through the regulation of γ’’ formation, mechanical properties can be optimized to suit challenging applications.
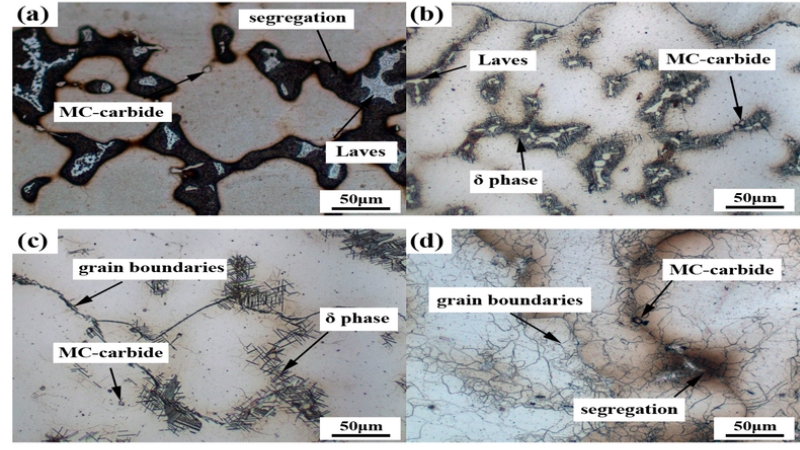
Carbides (MC, M₂C, M₇C₃)
The carbides are mostly formed at the grain boundaries and weld them to stop slide. This enhances low-temperature diffusional creep resistance. You will observe decreased grain boundary deformation and increased dimensional stability. The alloy is also strengthened by carbides as a means of hindering dislocation movement around boundaries. Correct distribution of carbide guarantees enhanced toughness and increases life of components against mechanical and thermal load.

Deleterious Phases and Their Effects
δ Phase (Ni₃Nb, Orthorhombic)
The delta phase is formed between 700-1000 C and it is highest at 900 C. It normally forms slowly at the grain boundaries. Its existence decreases γ’’ content, decreasing hardenability and raising the propensity to hot cracking. Nevertheless, during forging, controlled δ phase can be formed at pin grain boundaries. It can be used to tune grain size and enhance structural uniformity, although special thermal control is required to prevent adverse mechanical performance.
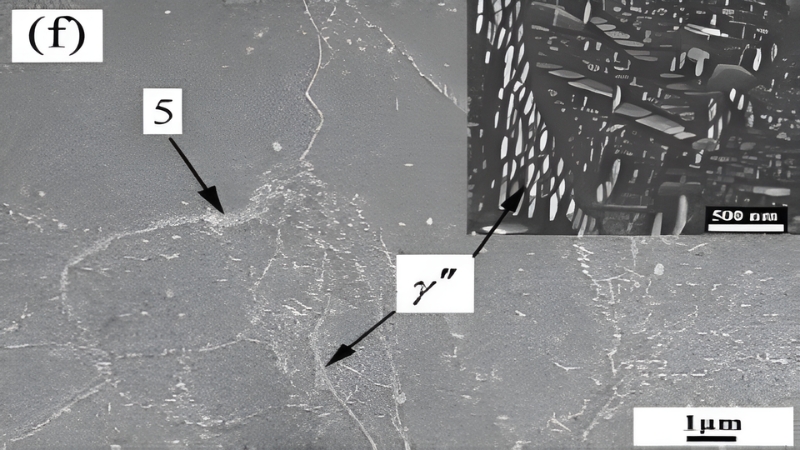
Laves Phase ((Ni, Fe, Cr)₂(Nb, Mo, Ti))
The delta phase is developed between 700-1000°C with a maximum of 900°C. It normally precipitates slowly at grain boundaries. Its presence decreases the content of γ’’, decreasing hardenability and enhancing the susceptibility of hot cracking. But the pin grain boundaries during forging can be pinned by means of controlled δ phase formation. This may be used to optimize grain size and structural uniformity, although close thermal considerations must be made to ensure adverse influences on mechanical performance are avoided.
Inconel 718 Material Properties – Mechanical Characteristics
- High Strength and Fatigue Resistance: Inconel 718 has an outstanding tensile strength and yield strength. Its cyclic loading capability by fatigue resistance can be depended on and the product can be able to withstand extreme stress.
- Creep Resistance: This alloy retains its structural integrity up to 700 o C. You have the advantage of low deformation when subjected to long life at elevated temperatures, best suited to turbine and aerospace applications.
- Stress-Rupture Behavior: Inconel 718 can resist stress rupture during both thermal and mechanical long-term loading. Prediction of performance through the service life of the component is possible.
- Hardness and Toughness: Heat-treated 718 exhibits controlled hardness and high toughness. These metrics need to be considered in choosing machining parameters and cutting strategies.
- Comparison with Other Ni-Based Superalloys: 718 is stronger and has a higher creep resistance than Inconel 625. You acquire better performance in high temperature application.
- CNC Machining Insight: Cuts speed, feed rate, and tool choice are influenced by its mechanical properties. You ought to select coated carbide or ceramic tools in order to achieve optimal efficiency.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
High content of chromium and nickel makes Inconel have excellent corrosion and oxidation resistance. It will do well in severe conditions such as high-temperature steam, acids and salt water. It is resistant to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking with long term durations. This resistance is important in aerospace, petrochemical, and nuclear power alternatives. In machining Inconel, it is important to note that it has protective features that should be maintained by treating its surface or subjecting it to post machining.
Heat Treatment and Processing
Inconel can greatly increase heat treatment performance and machinability. Solution annealing can be used to dissolve undesirable phases and increase ductility. When it is hardened by age γ’ and γ” phases are obtained, which gives it a greater strength. Adherence to temperature ranges and time optimizes micro structure and mechanical properties. In the case of CNC machining, the heat-treated stock minimizes residual stress and distortion, as well as guarantees accuracy. When processed properly, your machining processes are easier and more dependable.
What is Inconel Used for? – Applications of Inconel 718
- Aerospace: You use Inconel 718 in and compressor-airfoil engines. It is very strong and it has superior fatigue resistance making it safe when used in long-range high-temperature flights. CNC precision machining has both tight tolerances and intricate geometries of airfoils to maximize airflow.
- Rocket Engines: Inconel 718 can withstand high temperatures of combustion. It can be used in nozzles, combustion chambers, and thrust components. Precision machining guarantees accurate shapes and smooth walls, which is crucial in the fuel economy and the stresses distribution.
- Power Generation: Steam-line pipes, and nuclear reactor parts may be made of Inconel 718. Its special combination of high temperature strength and resistance to corrosion is advantageous to you because it will be reliable when under stress. CNC machining ensures smooth diameters and internal shapes essential to the efficiency of fluid flow.
- Petrochemical Industry: Inconel 718 is used in fasteners, valves, springs in chemical plants. On its resistance to fatigue and corrosioniveness you depend to eliminate failures at severe chemical exposures and high pressure.
- Why Preferred: It is the special combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and fatigue endurance, which is appropriate in the harsh environment. CNC machining opens the door to precision and consistency which you require on important use.
Machining Considerations for Inconel 718
Challenges in CNC Machining
CNC machining Inconel has a number of challenges that you should handle. It remains in a high state of work-hardening where cutting tools are quickly dulled, adding wear and shortening the tools in use. The toughness and ductility of the alloy cause vibrations and high temperatures in the cutting process, which influences the quality of the surface. You also encounter tool chipping and built up edges provided the feeds, velocities and coolants have not been optimized to achieve steady machining operations.
Best Practices in CNC Machining
The materials can be made of high-speed steel or carbide tools to be the most durable and precise in obtaining the best results CNC machining. The effectiveness of coolant should be treated with proper application to lower thermal stress and avoid wear of the tool. Turning, milling, drilling and Swiss-type machining are done step-by-step to be able to maintain uniform quality. Tight tolerances are required of you, and it is particularly required in the aerospace, medical, and energy markets where precision is paramount. With the correct tools, cooling, and methodic techniques, you can be able to increase economy and surface finish as well as overall part reliability.
Benefits of CNC Swiss Machining for IN718
- Tight Tolerances: Tolerances are very fine with tolerances that are as small as ± 0.0002 mm. This accuracy provides parts that fit well in important assemblies that minimize rework.
- Smooth Surface Finishes: CNC Swiss machining provides an excellent surface quality with Ра as small as 0.05 μm. You enjoy less after-process and higher component performance.
- Small, Complex Geometries and Micro-Holes: You are able to manufacture small, complicated geometries as well as micro-holes. The capability is best suited in aerospace, medical and high-performance engineering parts.
- High-Volume Production with Uniform Quality: Swiss machines are able to control uniformity in hundreds or thousands of parts. Production can be scaled and yet maintaining the exacting standards without loss of the tolerances.
- Exceptional High-Temperature Strength and Creep Resistance: IN718 exhibits good structural integrity during extremes of heat and against long-term stress. You depend on these properties including turbine blades, aerospace fittings, and engine components.
- High Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance: IN718 components Swiss-machined parts are resistant to rough chemical, marine, and high temperature environments. You get extended service and less maintenance in hard environments.
- Compatible with Precision CNC Machining of Complex Components: You are able to 100% take advantage of CNC Swiss of their advanced geometries and complex designs. This will result in compatibility of IN718 parts with even the most demanding engineering requirements.
Limitations
There are a number of considerations that you need to make when machining or using Inconel. Its toughness and quick work hardening also makes it difficult to cut and hastens the wear on the tool. There are also greater material costs than conventional stainless steels which impact project budgets. Also, the inadequate heat treatment process may form undesirable phases that result in lower strength and corrosion resistance. To prevent such problems, you will need to observe accurate handling and processing procedures.
Comparison with Other Superalloys
Property / Aspect | Inconel 718 | Inconel 625 | Waspaloy | Haynes 282 |
Composition | Ni-Cr-Fe-Nb | Ni-Cr-Mo | Ni-Cr-Co-Ti | Ni-Cr-Co |
Tensile Strength (MPa) | 1,270 @ 25°C | 827 @ 25°C | 1,050 @ 25°C | 1,100 @ 25°C |
Creep Resistance | Excellent (650–700°C) | Moderate | Excellent (700°C) | High |
Fatigue Performance | High | Moderate | High | High |
Corrosion Resistance | Good in oxidizing & marine environments | Excellent in marine & chemical environments | Moderate | Excellent |
Work Hardening / Machining | High work hardening, challenging | Moderate | High | Moderate |
Tool Life in CNC Machining | Shorter; carbide/ceramic preferred | Longer than 718 | Short; specialized tools required | Moderate; carbide tools effective |
Part Complexity Handling | Excellent for precision components | Suitable for medium complexity | High; difficult geometries | Good for complex geometries |
Use-Case Guidance | Aerospace turbine blades, cryogenic tanks, high-stress components | Chemical, marine, heat exchangers | Gas turbine discs, jet engine components | Aerospace and high-temperature structural parts |
Heat Treatment Sensitivity | High; solution and aging critical | Moderate | High | Moderate |
Preferred CNC Applications | Precision rotating parts, turbine disks, rocket motor cases | Marine valves, chemical reactors | Engine disks, high-temp blades | Aerospace structural components, engine frames |
Conclusion
To sum up, Inconel 718 is a superior blend of strength, corrosion resistance and high-temperature operation and thus, it is the best choice in vital aerospace, generation, and petrochemical parts. Its machining difficulties which are work hardening and tool wear must be handled with precision, proper tooling, and efficient CNC methods. You can maximize the potential of IN718 by knowing its metallurgy, heat treatment, and optimum machining. The collaboration with experienced CNC specialists provides high precision, durable, and reliable parts that are used in demanding applications.
